Fig. 3.
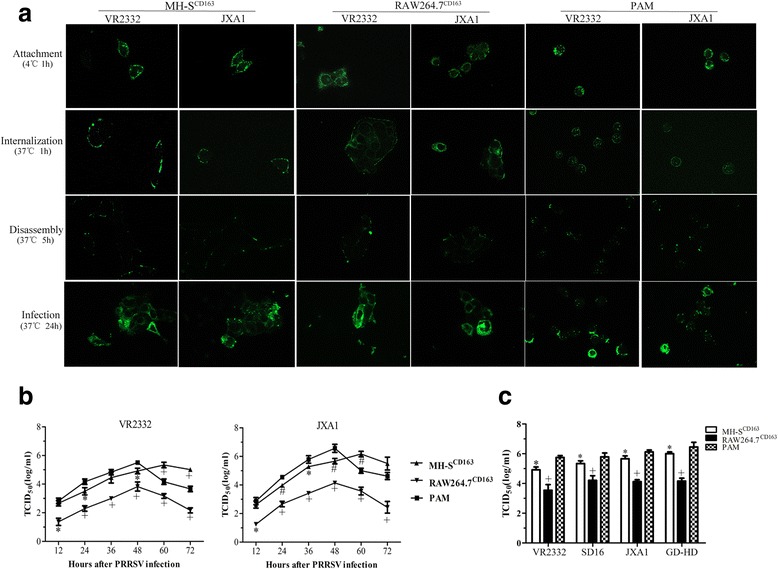
Susceptibility of MH-SCD163 and RAW264.7CD163 cell lines to various genotype 2 PRRSV isolates. a MH-SCD163 and RAW264.7CD163 cell lines and PAMs were inoculated with JXA1 and VR-2332 at 10 MOI. Various sequential stages of the viral replication cycle were measured by immunofluorescence staining of virus using anti-PRRSV N protein-specific mAb. Images are representative of three independent experiments. b PRRSV replication in MH-SCD163 and RAW264.7CD163 cells. The MH-SCD163 cells (triangle), RAW264.7CD163 cells (inverted triangle ) and PAMs (square) were inoculated with JXA1 and VR-2332 at 0.1 MOI. The lysate of each infected cell line at the indicated time points was collected and titrated on MARC-145. Values represent the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; #, P < 0.01; +, P < 0.001. c The MH-SCD163 and RAW264.7CD163 cells, parental cell lines and PAMs were inoculated with various PRRSV isolates (VR-2332, SD16, JXA1 and GD-HD) at 0.1 MOI. The lysate of each cell line infected with each indicated PRRSV isolate was collected at 48 hpi and titrated on MARC-145 cells. Values indicate the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; #, P < 0.01; +, P < 0.001
