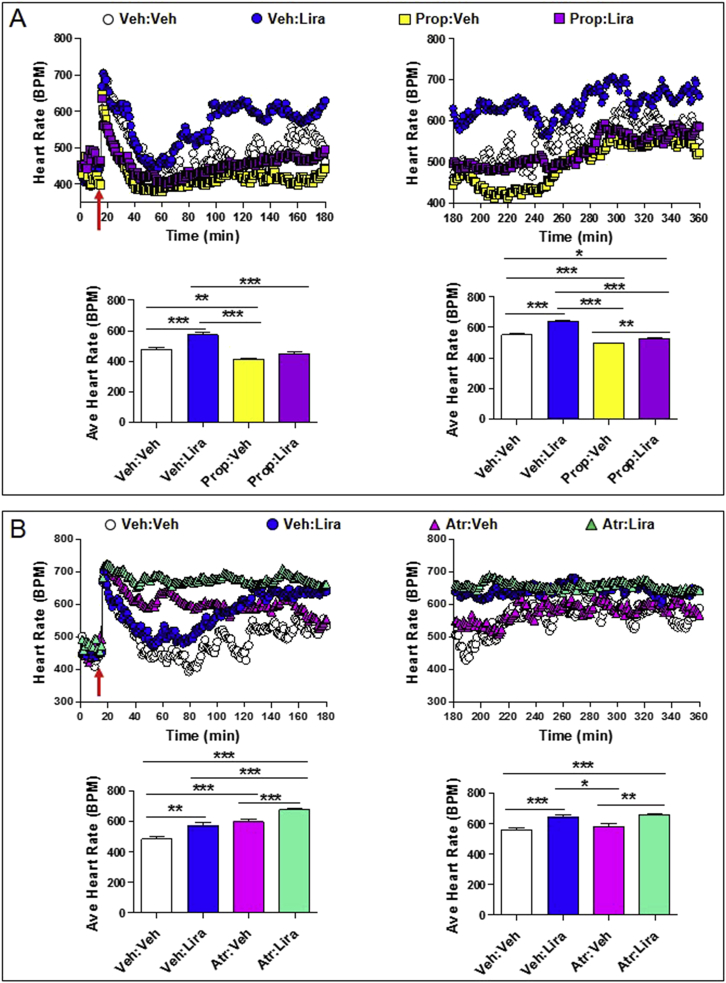
Figure 4.
Autonomic nervous system-dependent effects of liraglutide on heart rate. Heart rate (A and B; upper panels) and average heart rate (A and B; lower panels) over a 2–3 h interval in conscious, freely moving wild-type mice following a single ip injection of vehicle (Veh) or liraglutide (Lira; 30 μg/kg), in the presence or absence of propranolol (Prop; 5 mg/kg ip; sympathetic nervous system inhibitor) or atropine (Atr; 2 mg/kg ip; parasympathetic nervous system inhibitor). In (A) and (B), propranolol or atropine was administered at the same time as vehicle or liraglutide (red arrow; at time = 15 min). For (A) and (B), data in panels on the left are from the first 3 h (0–180 min) of heart rate recordings and data in panels on the right are from 3 to 6 h (180–360 min) after treatment administration. The average heart rate data for (A) and (B) lower left panels was calculated from 60 to 180 min or 40–180 min, respectively, when heart rates were stabilized following ip injections. Values are mean ± SE; n = 5–8 mice/group. Error bars have been purposely omitted from the heart rate data. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 (One-way ANOVA). Body weights (g) are 33.0, 32.0, 30.0, 34.0, and 30.0 for mice in (A) and 34.5, 36.6, 34.0, 35.2, 35.0, 32.2, 35.6, and 32.2 for mice in (B).