Figure 4.
LNT- and LFA-Induced Inflammatory Lesions Progress to Malignant Mesothelioma with Disruption of Cdkn2a Gene and Encoded Proteins
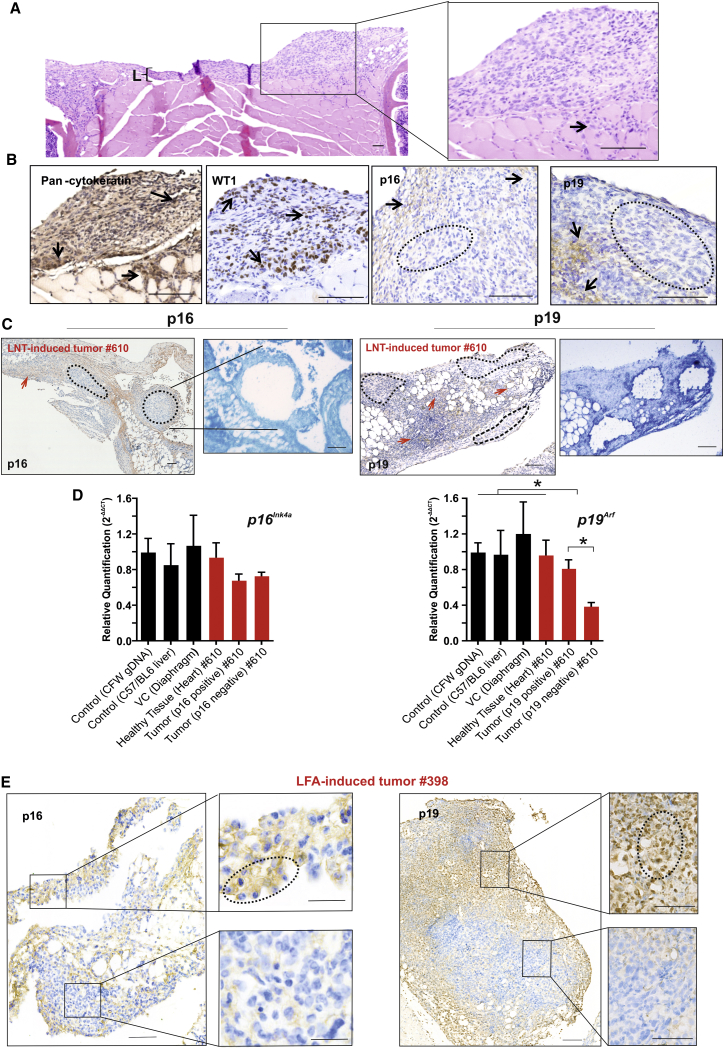
(A) LNT-induced mesothelioma at 12 months post-injection (animal ID: no. 610). The callout shows the mesothelioma composed of pleomorphic epithelioid tumor cells infiltrating into the underlying muscle (arrow). Adjacent to the tumor is an inflammatory lesion (L). Scale bars, 100 μm.
(B) Immunostaining of LNT-induced mesothelioma (animal ID: no. 610). Tumor cells stained positively for the mesothelial cell markers pan-cytokeratin and WT1 (arrows); the tumor areas stained positively (arrows) or negatively (circle) for the Cdkn2a-encoded proteins p16 and p19. Scale bars, 100 μm.
(C) Immunostaining of LNT-induced tumor (animal ID: no. 610) for p16 and p19. Negatively (circled) and positively (red arrows) stained areas were dissected and collected by power-assisted laser micro-dissection (PALM) for gDNA extraction and qPCR analysis. Callouts show a subsequent crystal violet-stained section of tumor after collection of selected areas. Scale bars, 100 μm.
(D) Relative quantification (mean of 2−ΔΔCT) of p16Ink4a and p19Arf gene copy number in gDNA from micro-dissected tumor and healthy tissue from the same animal or VC, showing allelic loss of p19Arf in p19-negative tumor areas compared to controls or p19-positive tumor areas. Graphs show mean ± SD; ∗p < 0.05 (significant difference is defined by Z score analysis; see also STAR Methods).
(E) Immunostaining of LFA-induced tumor (animal ID: no. 398) for p16 and p19 protein. Callouts show positively stained areas (circled) in the upper panels and negatively stained areas in the lower panels that were dissected and collected by PALM for gDNA extraction and qPCR analysis (see Figure S6C). Scale bars, 100 μm.
See also Figures S5–S7.