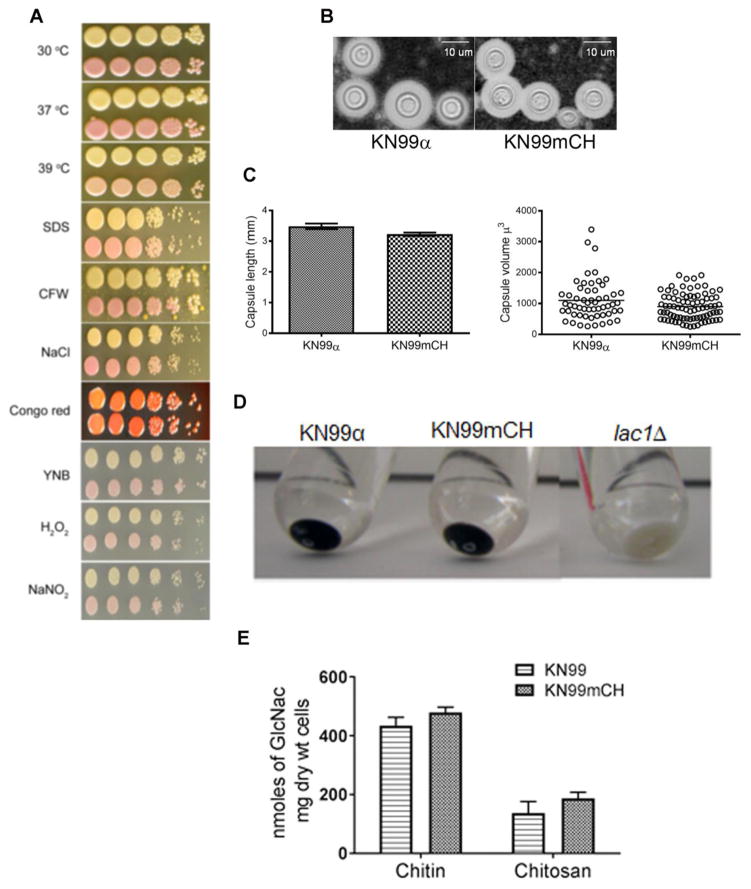
Fig. 3. KN99mCH grows like KN99α under various in vitro stress conditions and shows similar virulence trait expression.
A: Comparison of the growth of KN99α and KN99mCH strain under various in vitro stress conditions. C. neoformans strains were grown to mid log phase in YPD. Cells were harvested and diluted to OD650 = 1.0. Cell suspension was serially diluted (10 fold) and 4 μL of the original and the diluted cell suspensions were spotted on YPD agar containing appropriate stress reagent. Plates were incubated at 30 oC except where noted. Plates were photographed after 5 days of incubation. Top row, KN99α; bottom row, KN99mCH. B: Visualization of the capsule after India ink staining of the strains which were incubated in capsule inducing conditions. C: Quantitative analysis of the capsule length and the volume between KN99α and KN99mCH. D Comparison of cell associated melanin after incubating the cells in melanin inducing medium. E: Chitin and chitosan content of the indicated strains grown to saturation in YPD. There was no significant difference between KN99α and KN99mCH after Bonferroni multiple comparison test employing two-way ANOVA using Graph Pad Prism 7 software. Mean of three independent biological experiments are plotted with standard deviation.