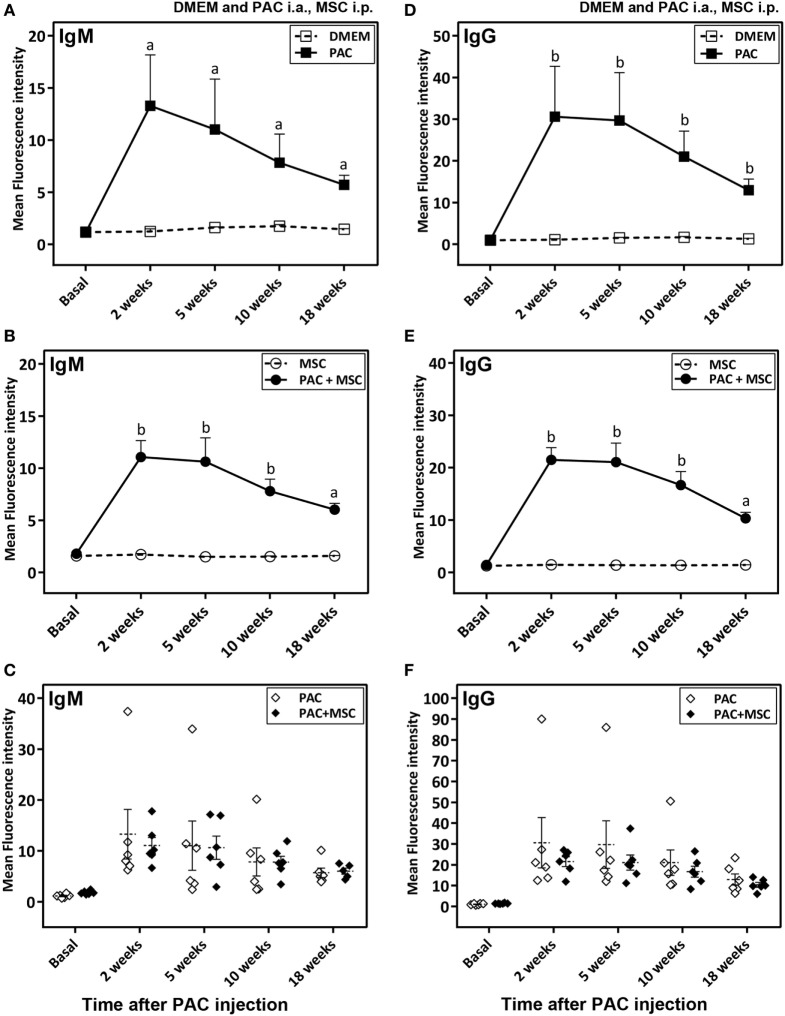
Figure 4.
Antibody response in Lewis rats injected intraarticularly (i.a.) with porcine articular chondrocytes (PAC) only or posttreated with mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) intraperitoneally (i.p.). A scheme of the experimental design comprising four different groups is shown in Figure S1C in Supplementary Material. In particular, one cohort received only DMEM i.a., another only PAC i.a., another was injected with MSC i.p. 3 weeks after PAC i.a. injection, whereas the corresponding control received only MSC i.p. at the same time. All were followed-up for 18 weeks. Anti-PAC IgM (A–C) and IgG (D–F) antibody reactivity was determined by flow cytometry for all rat sera (0.5% final dilution) collected at baseline and at 2, 5, 10, and 18 weeks after PAC injection. The mean ± SEM of mean FL-1 fluorescence intensity after subtracting the background (reactivity of secondary antibody alone) is shown (n = 5 for DMEM and MSC cohorts; n = 6 for PAC and PAC + MSC cohorts). Statistically significant differences were observed using the Mann–Whitney U test for the 2-week time point, but not the baseline, for both IgM and IgG relative to corresponding levels of the control cohort (ap < 0.01, bp < 0.005). No significant differences were detected when results of the PAC and PAC + MSC cohorts were compared using the Mann–Whitney U test (C,F).