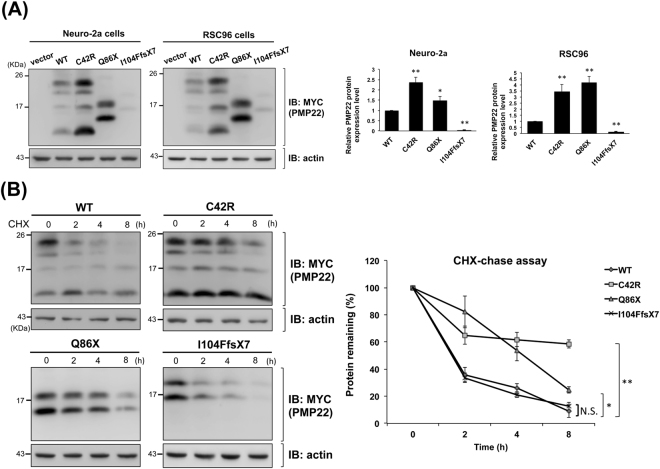
Figure 2.
In vitro characterization of the wide-type (WT), C42R, Q86X, and I104FfsX7 mutant PMP22 proteins. (A) Representative Western blot analysis and densitometric quantification of steady-state PMP22 expression in the Neuro-2a cells and RSC96 cells. Cells were transfected with WT or mutant PMP22 expression plasmids. Actin was used as a loading control. The error bars indicate standard error of the mean (SEM) from 3 independent experiments. The asterisks indicate statistically significant differences (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01). (B) Analyses of the stability of the WT and mutant PMP22 proteins. Neuro-2a cells were transfected with WT or mutant PMP22 expression plasmids for 48 hours and then subjected to cycloheximide (CHX)-chase assays. Representive Western blots are shown. All values are shown as means ± SEM (n = 3). The asterisks indicate statistically significant differences (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, NS = not significant).