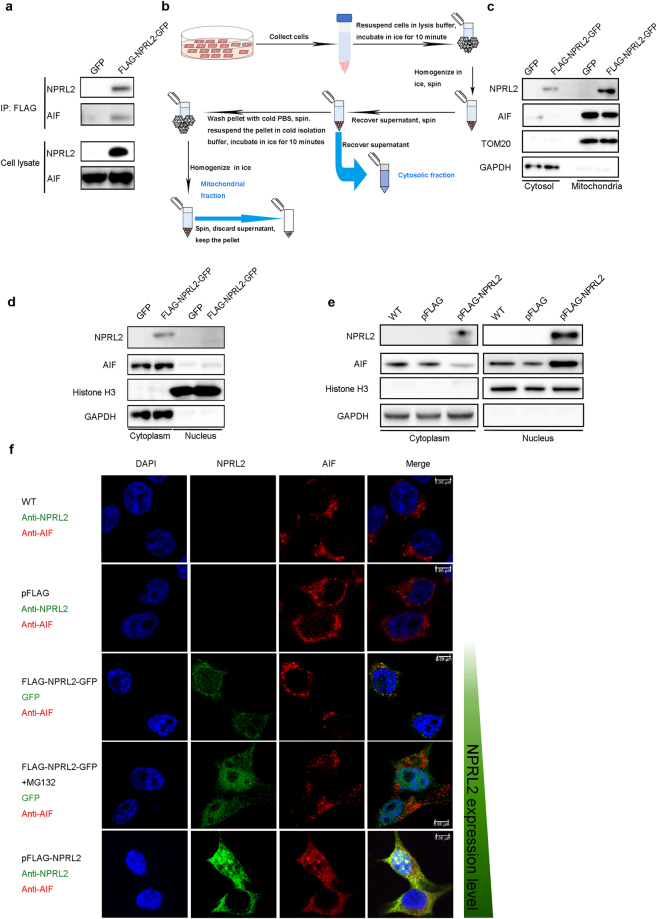
Figure 3.
Overexpression of NPRL2 promotes interaction with AIF and induces AIF translocation to the nucleus. (a) NPRL2 interacts with AIF. Immunoprecipitates were prepared from HEK293 cells stably expressing GFP or FLAG-NPRL2-GFP and analyzed by immunoblotting for the indicated proteins. (b) The scheme of subcellular fractionation experiment used for the detection of NPRL2 localization. (c) Overexpressed NPRL2 localizes to mitochondria. The subcellular localization of NPRL2 was detected by immunoblotting with antibodies against indicated proteins in the mitochondrial and cytosolic extracts. TOM20 was used as mitochondrial marker and GAPDH as cytosolic marker. (d–f) Overexpression of the NPRL2 induces re-localization of NPRL2 and AIF to the nucleus. The cytoplasm and nuclear extracts were prepared from HEK293 cells either stably expressing FLAG-NPRL2-GFP or GFP (d) or transfected with pFLAG or pFLAG-NPRL2 plasmids (e) and analyzed by immunoblotting for the indicated proteins with Histone H3 as a marker for the nucleus and GAPDH as a marker for the cytoplasm. (f) Immunofluorescence analysis of localization of NPRL2 and AIF localization. Nucleus is stained with DAPI (blue); NPRL2 (green) is detected either via GFP in case of HEK293 stably expressing FLAG-NPRL2-GFP or with immunofluorescence with anti-NPRL2 antibody; AIF (red) is detected with anti-AIF antibody. Scale bar, 5 μm. The increased level of NPRL2 expression in these experiments is indicated with growing green bar to the right of image panels.