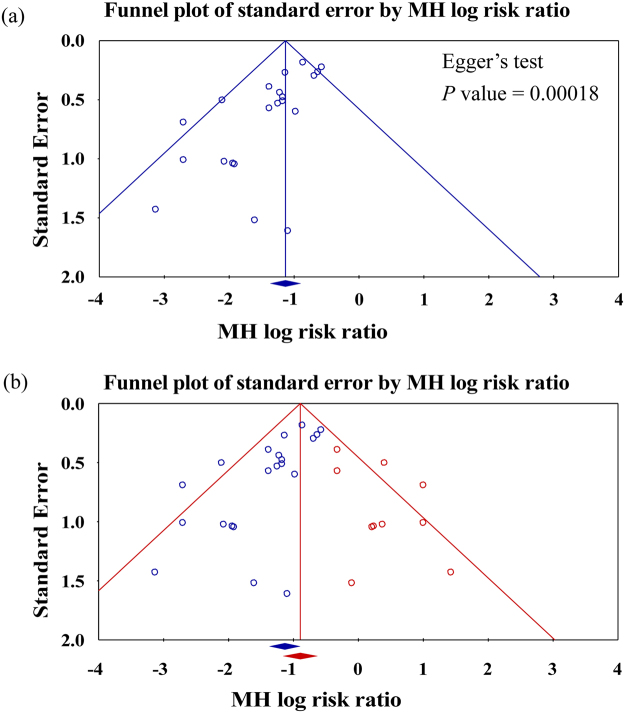
Figure 5.
Funnel plots was applied to assess publication bias which were plotted in the log risk ratios against their standard errors and estimating the number of missing studies that might exist in a meta-analysis and the effect that these studies might have had on its outcome. (a) Funnel plot with 95% confidence limits for testing publication bias; (b) Funnel plot of all studies with 95% CI, including hypothetical studies using ‘trim and fill’ method (in red) for adjusting publication bias. After adjusting for missing studies, we noted that the point estimate of the overall effect size is approximately correct and coverage of the effect size confidence intervals is substantially improved. The results showed that publication bias or another confounding variable should be considered, but would not be a major influencing factor for the intervention effect. That is, the publication bias did not affect our major outcomes.