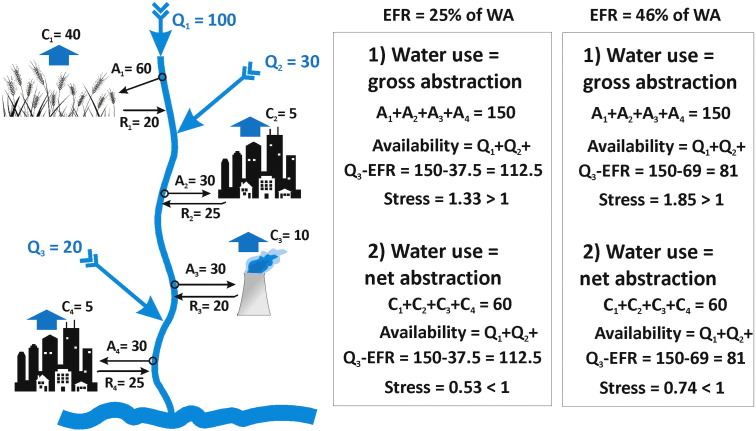
Fig. 4.
Adaptation of Fig. 2, by incorporating EFR. Two options are presented: EFR equal to 25% or 46% of water availability (WA), based upon global values listed by (Pastor et al., 2014). For both options, a clear distinction in WS quantification is seen when water use is gross or net abstraction. When EFR = 25% of WA, stress is computed to be 1.33 (larger than threshold value 1, so a situation with violation of EFR) for a gross abstraction of 150 units, whereas the stress value is 0.53 (smaller than threshold value 1, so a situation without violation of EFR) for a net abstraction of 60 units. When EFR = 46% of WA, the same observations are made but higher stress values are computed, because EFR volumes are set higher.