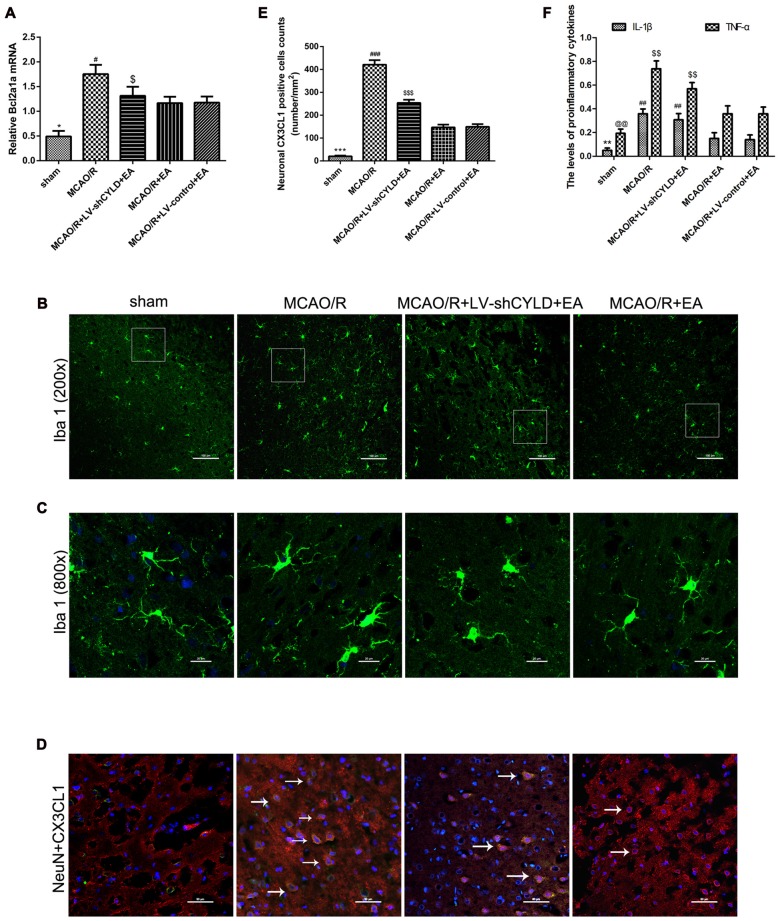
Figure 6.
CYLD silencing partially weakens effects of EA on anti-inflammatory injury after 24 h reperfusion. (A) Bcl2a1a (microglia) mRNA was measured with RT-qPCR in the peri-ischemic cortices of MCAO/R, MCAO/R + LV-shCYLD + EA and MCAO/R + EA group rats and the sham cortices. β-actin was a loading control. *p < 0.001 vs. MCAO/R group, #p < 0.05, $p < 0.001 vs. MCAO/R + EA group, n = 6/group. (B) Immunofluorescence staining showed that CYLD silencing partially weakened the effect of EA on repressing activated microglia (Iba1, green), n = 9/group (Scale bar = 100 μm). (C) Magnification of (B) shows activated morphology of microglia (Scale bar = 20 μm). (D) Neuronal CX3CL1 positive cells (white arrows) of the peri-ischemic cortex from merged image (co-expression of neurons and CX3CL1) after ischemic stroke (Scale bar = 50 μm). (E) Neuronal CX3CL1 positive cell counts were expressed as number/mm2. ***p < 0.001 vs. MCAO/R group, ###p < 0.05, $$$p < 0.001 vs. MCAO/R + EA group. (F) IL-1β and TNF-α were detected using ELISA. **p < 0.05, @@p < 0.001 vs. MCAO/R group, ##p < 0.05, $$p < 0.05 vs. MCAO/R + EA group, n = 5/group.