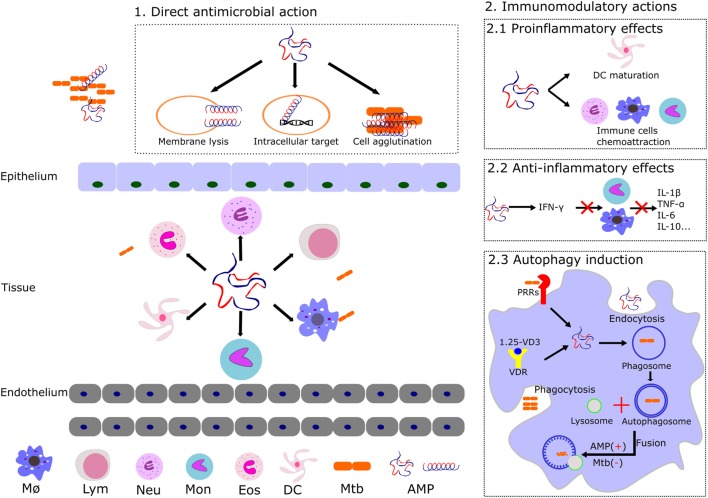
Figure 2.
Illustration of the distinct reported mechanism of action of AMPs expressed by the host innate immune cells. The main AMP antimicrobial and immunomodulatory activities are shown: (1) AMPs can trigger the cell lysis, target intracellular key processes (described in Figure 1), and/or agglutinate the bacterial cells. (2) Main AMPs’ immunomodulatory actions that promote the mycobacterial clearance are illustrated. Induction of pro and anti-inflammatory activities contributes to the host defense by regulation of cytokines and chemokines expression and induction of innate cell maturation. AMPs can also intervene in the autophagosome and phagolysosome formation during autophagy. Abbreviations: MØ, macrophages; Lym, lymphocytes; Neu, neutrophils; Mon, monocytes; Eos, eosinophils; DC, dendritic cells; Mtb, Mycobacterium tuberculosis; AMP, antimicrobial peptides; VD3, vitamin D3; VDR, vitamin D receptor; PRRs, pattern recognition receptors.