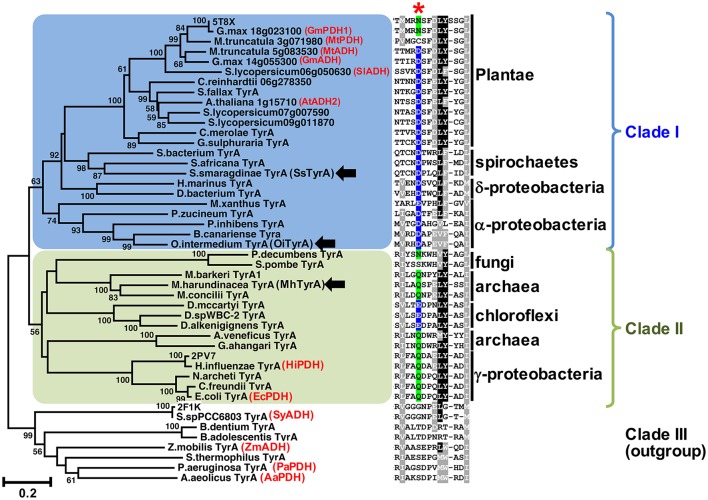
Figure 2.
The conserved acidic residue at 222 among clade I TyrA orthologs from plants, algae, and closely-related bacteria. Structure-guided phylogenetic analysis of plant and microbial TyrAs. Three distinct clades are formed; clade I contains all plant TyrAs and closely-related microbes (blue), clade II contains bacteria, archaea, and fungi TyrAs (green), and clade III, which was used as an outgroup. Enzymes characterized in this study are marked by black arrows. Structures used to guide the alignment are labeled with their PDB IDs. Previously characterized TyrAs are labeled in red with their preferred PDH or ADH activity. Scale bar represents number of substitutions per branch length. A trimmed amino acid alignment of corresponding sequences shows a conserved acidic residue (Asp or Glu, highlighted in blue) among clade I, which is replaced with a non-acidic Asn or Gln residue (highlighted in green) in most clade II at the corresponding 222 position marked with a red star. Identical amino acids present in >50%, black shading; biochemically similar residues present in >50% of the sequences, gray shading.