FIGURE 2.
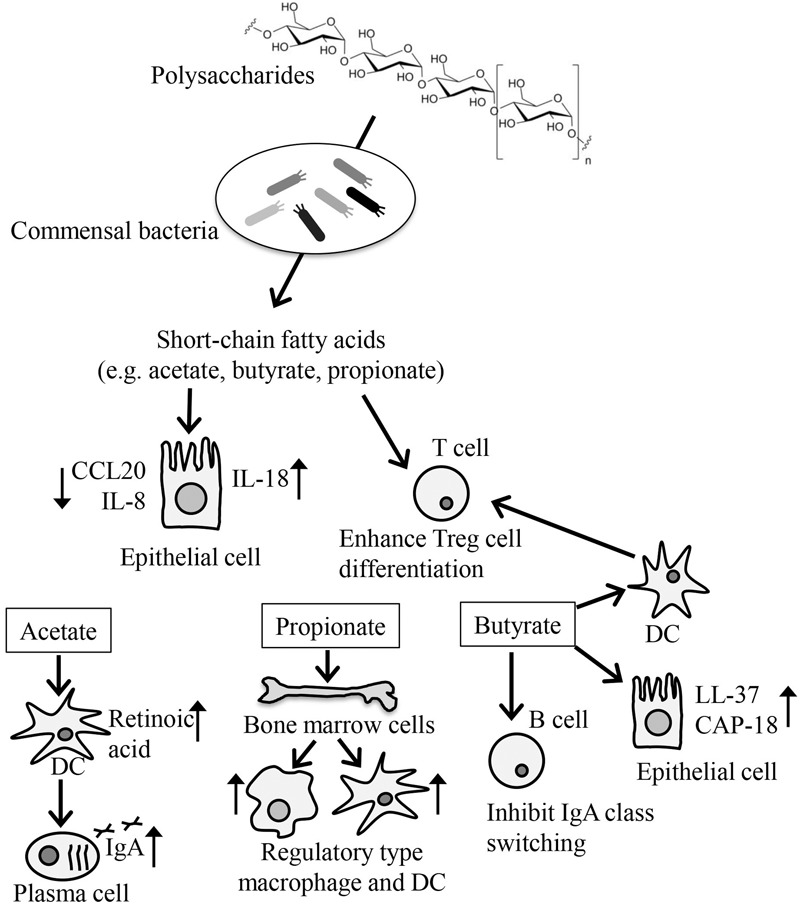
Modification of immune responses by SCFAs produced by microbial fermentation. SCFAs are produced by bacterial fermentation of dietary indigestible polysaccharides and participate in the regulation of energy metabolism, cellular function, and differentiation. SCFAs, such as acetate, butyrate, and propionate, are taken up by IECs, where they inhibit the production of inflammatory cytokines such as CCL20 and IL-8 and enhance the production of IL-18, which is involved in IEC integrity. Butyrate participates in the production of antimicrobial peptides such as LL-37 and CAP-18. SCFAs also directly enhance the differentiation of Treg cells. Butyrate acts on DCs to enhance DC-induced Treg cell differentiation. Acetate enhances the production of retinoic acids from DCs, which promote IgA production, whereas butyrate inhibits the IgA class switching of B cells. Propionate enhances the generation of regulatory type of macrophages and DCs from bone marrow cells.
