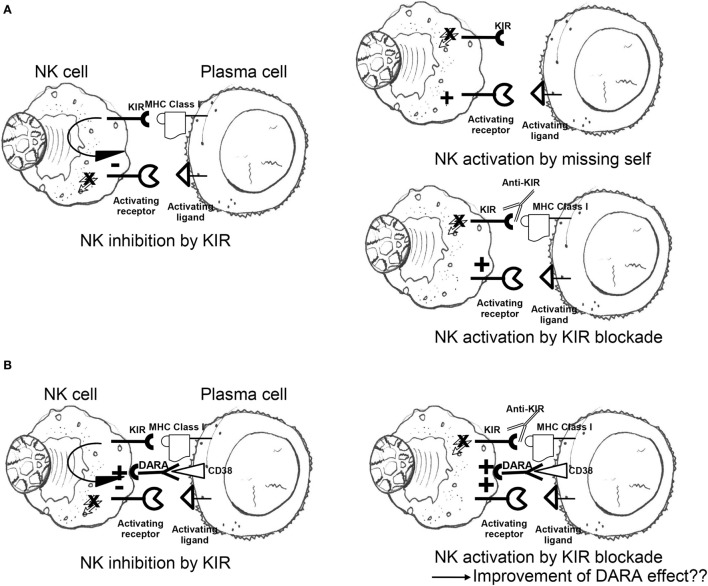
Figure 2.
(A) Engagement of self-MHC class I by inhibitory KIR results in dominant-negative signals blocking competing activation responses; lack of MHC class I molecules triggers NK cell killing (missing-self recognition); inhibitory KIR blockade by anti-KIR mAbs abrogates KIR-mediated inhibition regardless of MHC class I ligand expression on target surface (“induced” missing self). (B) Negative signals transduced by inhibitory KIR antagonize anti-CD38 (DARA)-induced antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, potentially dampening NK cytotoxicity to plasma cells; addition of KIR checkpoint inhibitors may potentiate the positive effects of DARA on NK cytotoxicity of malignant plasma cells (see also main text). NK, natural killer; KIR, killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; DARA, daratumumab.