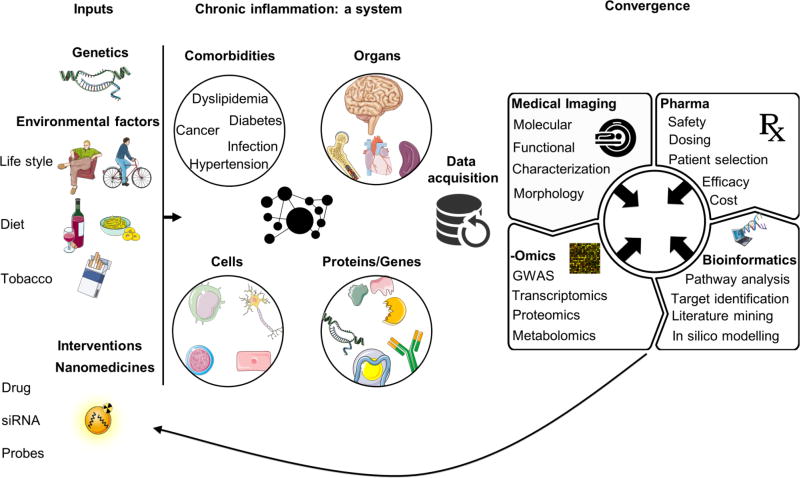
Fig. 5. Considerations for applying and developing nanomedicines for chronic inflammatory diseases.
Chronic inflammatory diseases are multifactorial disorders in which genetic background and environmental factors interact and affect different dynamic systems, including genes, signaling pathways, cells, and organs. Nanomedicine should be approached in a holistic way, in which nanodrugs’ systemic interactions are investigated, and can be used to visualize and/or modulate multiple processes. Data acquisition and convergence of nanomedicine with the different biomedical fields and big data (e.g. transcriptomics, proteomics, and genomics) can not only contribute to deciphering these complex diseases but also help to predict the efficacy of nanomedicines and to develop clinically relevant products.