Fig. 1.
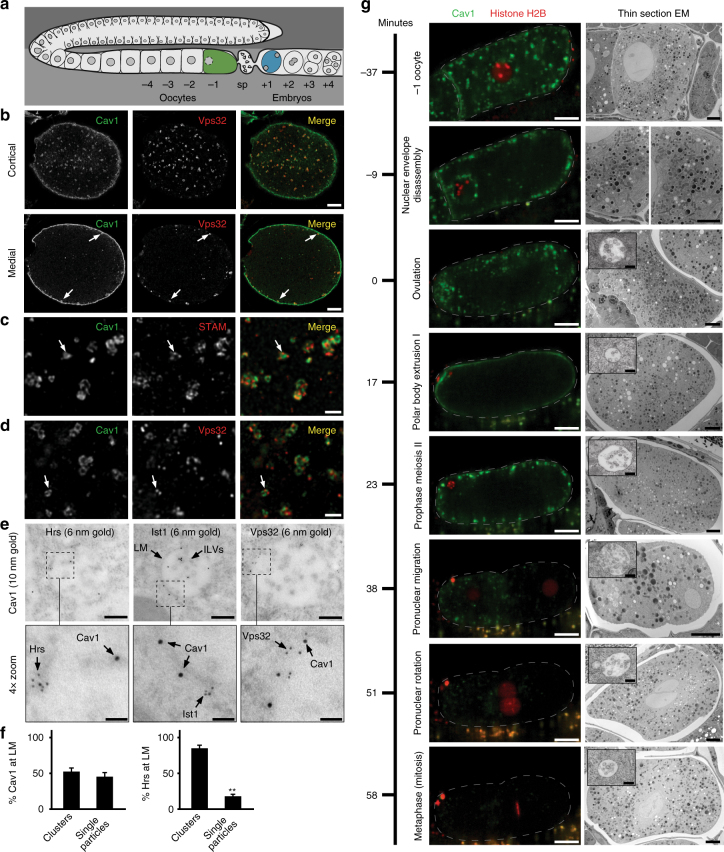
De novo MVE biogenesis initiates near the cortex of C. elegans zygotes. a Cartoon depicting the C. elegans reproductive system. Oocytes are fertilized as they pass through the spermatheca (sp) and develop as embryos within the uterus. b Embryos expressing GFP::Cav1 were fixed and stained using antibodies directed against GFP and Vps32 and imaged using confocal microscopy (n = 6). Representative images are shown. Arrows highlight cortical endosomes that are positive for both Cav1 and Vps32. Bars, 5 μm. c, d Higher magnification of embryos described in panel b imaged using STED microscopy. Arrows highlight the presence of endosomal subdomains harboring STAM (n = 5, c; ESCRT-0) or Vps32 (n = 5, panel d; ESCRT-III), while Cav1 is more uniformly distributed. Bars, 1 μm. e Animals were high-pressure frozen and processed for immunogold labeling using antibodies directed against Hrs (6 nm gold, left, n = 28 MVEs), Ist1 (6 nm gold, middle, n = 16 MVEs), or Vps32 (6 nm gold, right, n = 11 MVEs), together with antibodies against GFP::Cav1 (10 nm gold). The limiting membrane (LM) and intralumenal vesicles (ILVs) are indicated with arrows (top, middle panel). Representative images are shown. Bars, 200 nm (top panels) and 50 nm (bottom panels). f Based on the distribution of gold labeling at the endosome limiting membrane (LM) described in panel e, the percentages of Cav1 and Hrs in clusters/subdomains (defined as 2 or more gold particles within 20 nm) or individual gold particles was quantified. Standard error of the mean is shown in each case. **p < 0.01, using a t-test. g Animals expressing GFP::Cav1 and RFP::His58 (Histone H2B) were imaged using time lapse confocal microscopy during ovulation and early embryogenesis (left panels; oocyte and embryo are outlined, n = 12 animals). Corresponding thin-section electron microscopy studies were conducted at the indicated time intervals (right panels). Representative images are shown. Bars, 10 μm (left panels), 4 μm (right panels), and 200 nm (right panel insets highlighting MVEs)