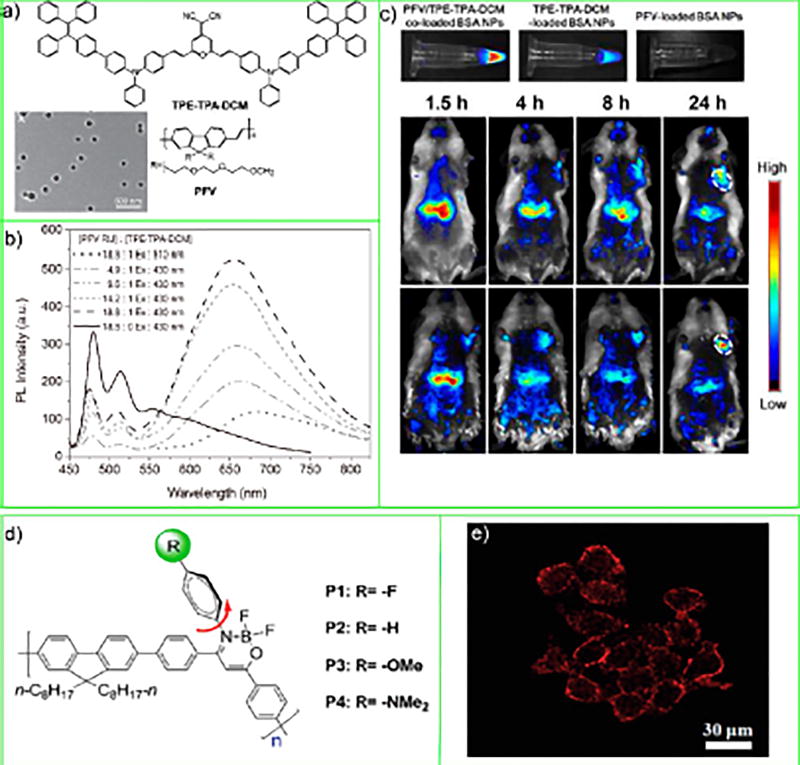
Figure 7.
(a) Chemical structures of PFV host polymer and TPE-TPA-DCM molecules and TEM image of the PFV/TPE-TPA-DCM coloaded BSA CPNs. (b) PL spectra of PFV/TPE-TPA-DCM coloaded BSA CPNs in water. (c) In vitro fluorescence images of aqueous solutions containing PFV/ TPE-TPA-DCM coloaded, TPE-TPA-DCM-loaded, and PFV-loaded BSA CPNs. In vivo fluorescence imaging of tumor-bearing mice after intravenous injection of PFV/TPE-TPA-DCM coloaded BSA CPNs (b) and PFV/TPE-TPA-DCM coloaded BSA-RGD CPNs. The white circles indicate the tumor sites. Reproduced in part from Ding, D.; Li, K.; Qin, W.; Zhan, R.; Hu, Y.; Liu, J.; Tang, B. Z.; Liu, B., Conjugated Polymer Amplified Far-Red/Near-Infrared Fluorescence from Nanoparticles with Aggregation-Induced Emission Characteristics for Targeted In Vivo Imaging. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2013, 2 (3), 500–507 (ref 57). Copyright 2013 Wiley. (d) Chemical structures of conjugated polymers P1-P4. (e) Confocal fluorescnece images of HeLa cells stained with P1 CPNs. Reproduced in part from Dai, C.; Yang, D.; Fu, X.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, C.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, L., Polym. Chem. 2015, 6 (28), 5070–5076 (ref 58), with permission of The Royal Society of Chemistry.