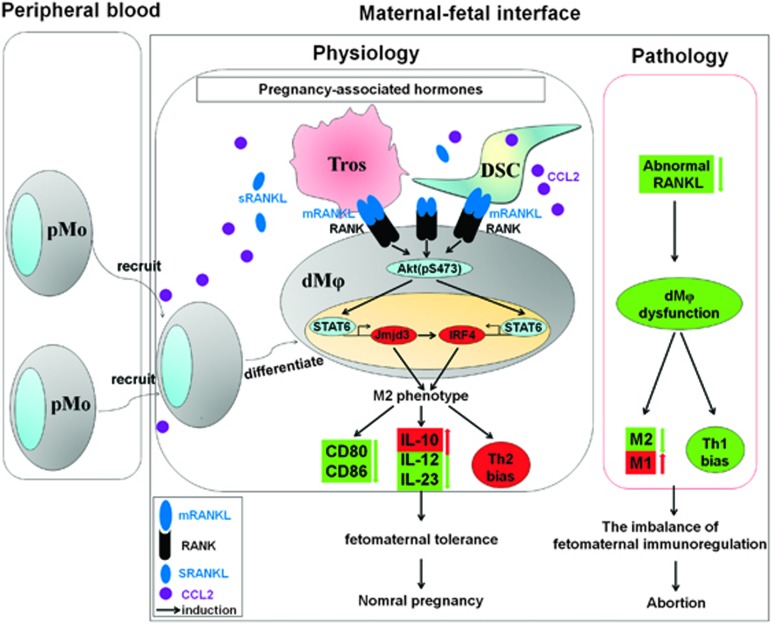
Figure 7.
RANKL-mediated harmonious dialog between the fetus and mother guarantees a smooth gestation by inducing decidual M2 macrophage polarization. Together with blastocyst implantation during normal pregnancy, PAHs trigger ESCs to differentiate into DSCs, further inducing high levels of RANKL expression and CCL2 release. The latter recruits more peripheral monocytes to the decidua. Embryonic trophoblasts that are deeply implanted in decidua can closely contact DSCs and DLCs. This dialog not only further increases RANKL expression in trophoblasts and DSCs, but it also enhances the sensitivity of RANK to RANKL by upregulating RANK expression on Mφ. Subsequently, the RANKL–RANK interaction drives Mφ to M2 differentiation (low expression of CD80 and CD86, high secretion of IL-10, and low level of IL-12 and IL-23) by activating Akt/STAT6-Jmjd3/IRF4 signaling. After education, these Mφs will create and maintain a maternal immune tolerance microenvironment (increase in Th2 and decrease in Th1). After the development of abnormally low RANKL expression at the maternal–fetal interface, the dysfunction of Mφ, the imbalance of maternal–fetal immune regulation and then abortion will occur. Tro: trophoblasts