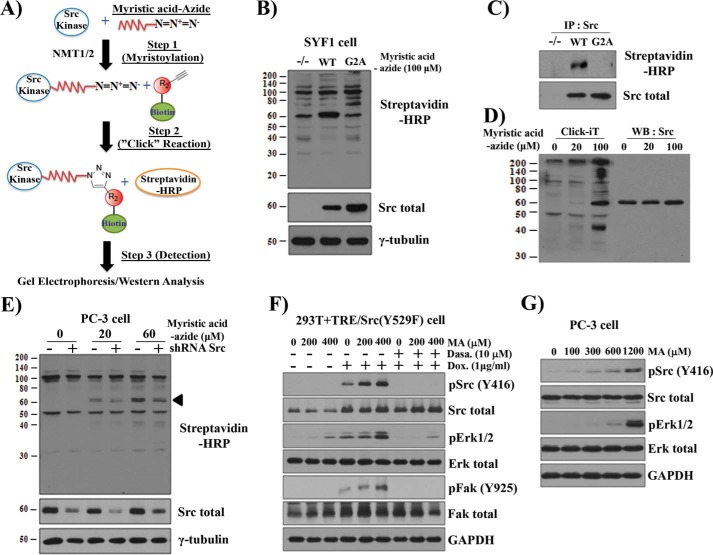
Figure 6.
Exogenous MA elevates myristoylated Src kinase and promotes Src oncogenic signaling. A, schematic of click chemistry to detect the myristoylation of Src kinase. Cells were grown with myristic acid-azide overnight. NMT1/2 catalyzes the cellular acylation of Src kinase. As a result, myristic acid-azide was processed intracellularly and incorporated into de novo synthesized Src kinase (Step 1). Myristic acid-azide–modified Src kinase in the cell lysate was reacted with a biotin-conjugated alkyne in vitro in a click reaction (Step 2). The biotin-myristoylated Src was immunoprecipitated and visualized by immunoblotting using streptavidin-HRP (Step 3). Total Src was visualized by immunoblotting. B, SYF1 (Src−/−Yes−/−Fyn−/−) cells expressing Src(WT), Src(G2A), or control were grown in medium containing 100 μm myristic acid-azide. Myristoylated proteins were detected by a click chemistry reaction. C, identification of myristoylated Src(WT) from click chemistry reactions by immunoprecipitation (IP, using a Src antibody) and immunoblotting with streptavidin-HRP. D, SYF1 cells expressing Src(WT) were cultured with 0, 20, and 100 μm of myristic acid-azide. Myristoylated proteins and the expression of Src were detected by click chemistry reactions (left) and immunoblotting (right). WB, Western blot. E, PC-3 cells expressing control or shRNA-Src were cultured with 0, 20, or 60 μm myristic acid-azide. The arrowhead indicates the band of Src kinase. F and G, 293T cells expressing doxycycline-inducible Src(Y529F) (293T+TRE/Src(Y529F)) were grown in DMEM with 2% BSA and treated with MA (F) with/without Dox (1 μg/ml) or dasatinib (10 nm) for 24 h. PC-3 cells were grown in F-12K medium with 2% BSA and treated with 0, 100, 300, 600, or 1200 μm MA overnight (G). The levels of total Src, pSrc(Tyr-416), total FAK, pFAK (Tyr-925), total Erk, and pErk1/2 were determined by immunoblotting. The data represent three independent experiments.