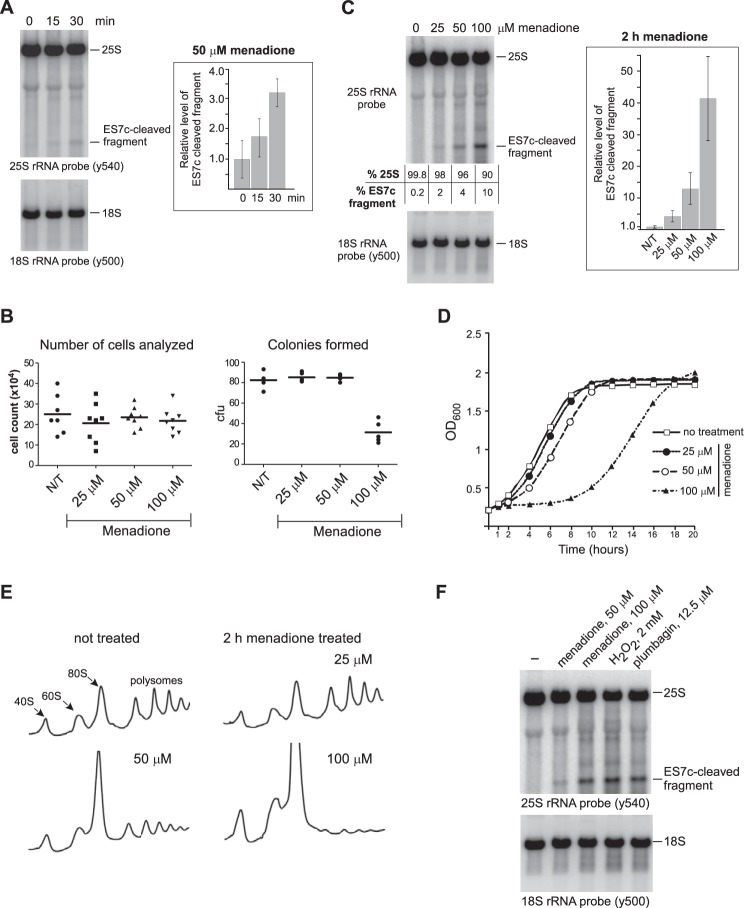
Figure 5.
ES7c cleavage occurs rapidly in response to oxidant doses that do not reduce cell viability. A, overnight culture of wild-type cells was diluted with YPDA to A600∼0.2 and grown for 4 h, and 50 μm menadione was added. RNA was extracted at the indicated time points and analyzed by Northern hybridization with rRNA probes. ES7c-cleaved fragment was quantified as described in Fig. 3B. The data show mean values of three independent experiments; the error bars represent S.D. B, cells grown as in A were treated with 25, 50, or 100 μm menadione for 2 h. To compare total cell numbers in each culture, the cells were counted using a hemocytometer (8 counts/culture; left panel). For the clonogenic assay (right panel), equal volumes of each culture were plated onto YPDA agar plates (5 replicates/culture). The plates were incubated at 30 °C for 3 days, and colonies formed on each plate were counted. The 100 μm menadione treatment was the only statistically significant condition (p < 0.0001, unpaired, two-tail t test) compared with the no-treatment (N/T) control, other treatments had no significant differences in the number of colony-forming units (cfu) relative to the no-treatment culture. C, rRNA cleavage in cells treated with menadione as in B. The ratio of the hybridization signals of the full-length 25S rRNA and the ES7c-cleaved fragment is indicated for each lane. The graph shows relative levels of ES7c-cleaved fragment normalized to 18S rRNA quantified in three biological replicates as described for Fig. 3B; the error bars represent S.D. D, growth curves of wild-type BY4741 cells in YPDA containing different menadione concentrations. Triplicate cultures in a 96-well plate were incubated at 30 °C with shaking. A600 measurements were recorded using a microplate reader; the data show the mean value at each time point. E, polysome traces for the wild-type strain treated with the indicated concentrations of menadione for 2 h. F, Northern analysis of rRNA from wild-type cells treated for 2 h with various oxidants at the indicated concentrations.