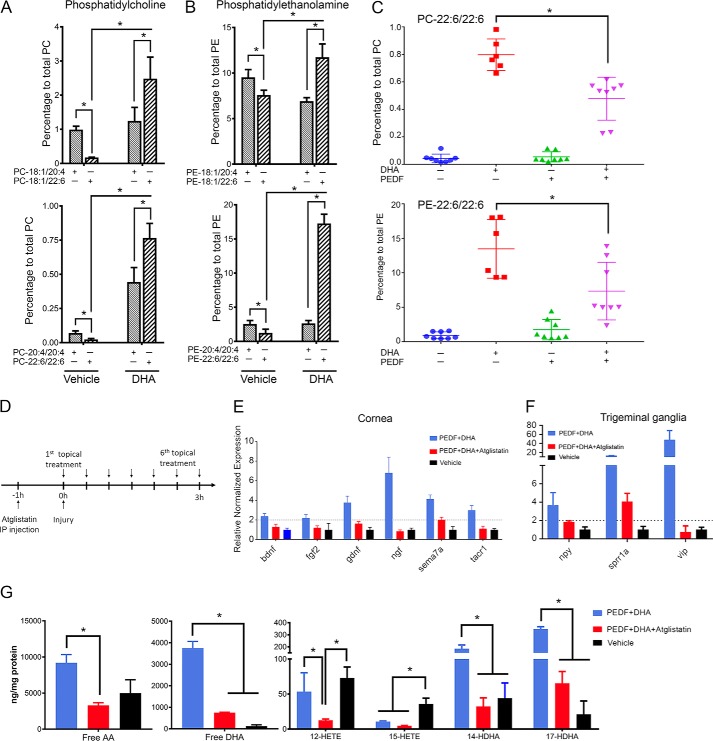
Figure 5.
DHA incorporation in corneal PC and PE molecular species, from basal to treated conditions. Effect of atglistatin on gene expression, release of DHA and AA, and synthesis of hydroxy-derivatives was examined. A and B, comparison of different molecular species of PC and PE in injured corneas in mice after 1 h of topical DHA treatment in vivo analyzed by LC-MS/MS. Each plot shows the percentage of specific PC/PE species in the vehicle- (left) and DHA (right)-treated corneas. Data were collected from eight corneas individually (one cornea/sample). *, p < 0.05 with the t test statistical analysis to compare two groups at 95% of the confidence level. C, quantification of 22:6/22:6-containing PCs and PEs in the presence of PEDF, DHA, and PEDF + DHA. Single data point represents one treated cornea. *, p < 0.05 with ANOVA analysis plus Fisher post hoc test at 95% of the confidence level. D, experimental design of mice treated with atglistatin injected (i.p.) before injury and topically treated with PEDF + DHA, PEDF + DHA + atglistatin, or vehicle after injury. E and F, gene expression analysis in corneas (E) and TG (F) at 3 h after injury and treatment. G, mass spectrometry-based lipidomic analysis of mouse corneas as explained under “Experimental procedures.” *, p < 0.05 with ANOVA analysis plus Fisher post hoc test at 95% of the confidence level. For lipid analysis, a pool of six corneas/sample was used. Bars represent the mean of three experiments ± S.D.