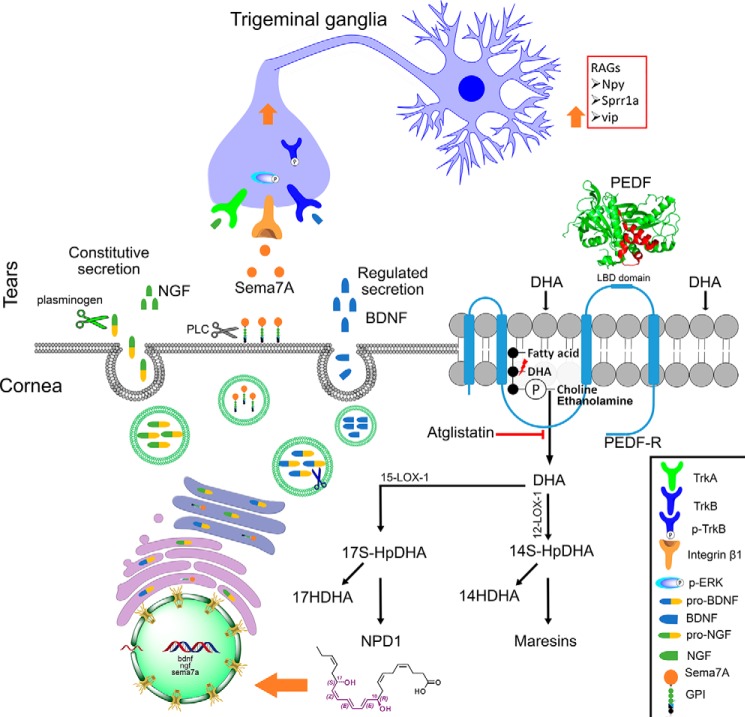
Figure 7.
Working model of the action of PEDF + DHA in enhancing corneal nerve regeneration. PEDF via its 44-mer neuroprotective domain (in red) activates PEDF-R in the cornea (amplify for clarification). This transmembrane receptor with iPLA2 activity released DHA, enriched in the sn-2 position of membrane phospholipids, by DHA supplementation. Mouse corneas express a 12- and 15-lipoxygenase (LOX) (55); DHA is converted to 17-HpDHA on the pathway to NPD1 by 15-LOX-1, and DHA is also converted to 14-HpDHA on the pathway to maresin-1 by 12-LOX-1. Docosanoids such as NPD1 (and possibly others not yet identified) induce the gene expression and protein levels of the neurotrophins NGF, BDNF, and Sema7A (all of which are secreted to tears), and of RAGs vip, npy, and sprr1a in the TG. Phosphorylation of TrkB and ERK 1/2 occurs in the TG as a result of BDNF and Sema7A secretion in the tear film. Inhibition of the phospholipase activity of the PEDF-R abolishes this signaling mechanism and corneal nerve regeneration.