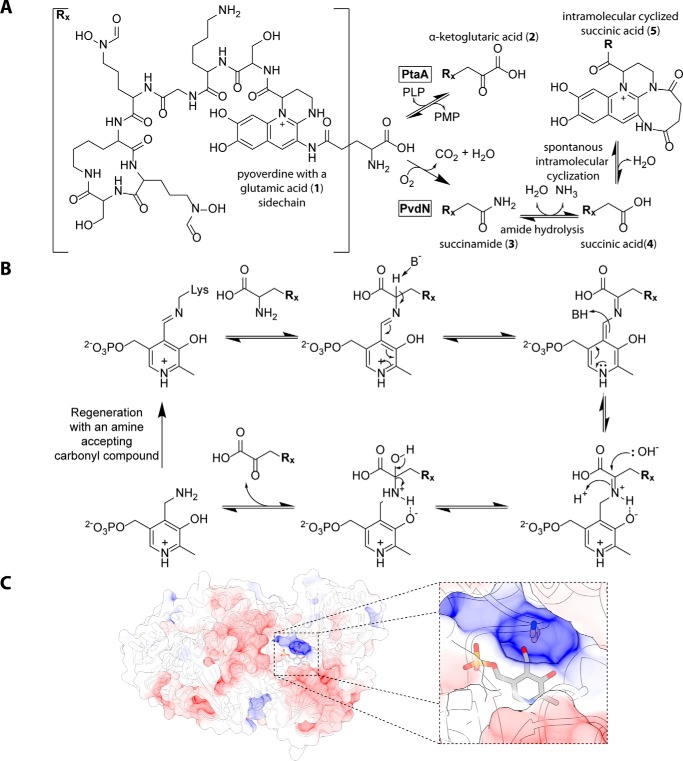
Figure 6.
Role and mechanism of PtaA in periplasmic pyoverdine tailoring. A, beginning from the glutamic acid variant (1) of PVDA506, two competing tailoring pathways are present. Transamination by PtaA results in the α-ketoglutaric acid variant (2) PVDA506, whereas the PvdN modification results in the succinamide variant (3), which can be partially hydrolyzed to the succinic acid (4) and then intramolecularly cyclized (6). B, proposed mechanism of transamination as catalyzed by PtaA in the periplasm, postulating a carbonyl compound for regeneration of PLP. C, structure of PtaA as calculated by homology modeling, highlighting the Lys-224 residue and the PLP cofactor. The model was visualized with UCSF Chimera.