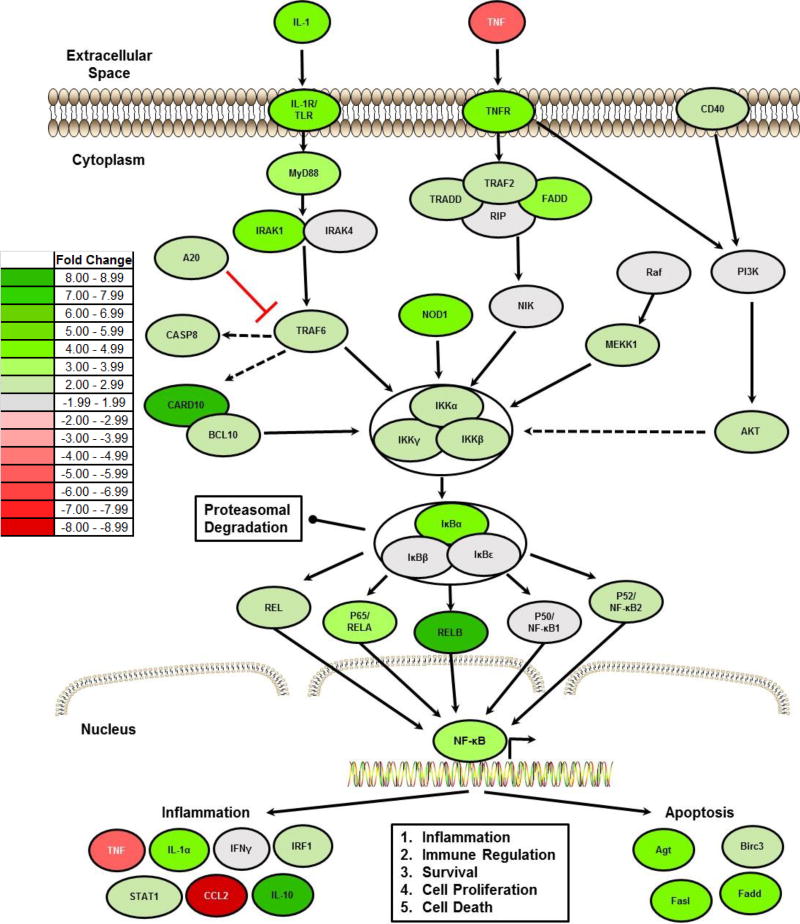
Figure 3. NLRX1 Negatively Regulates NF-κB Signaling Following TBI.
A) Heatmap schematic illustrating fold change in expression of all genes associated with NF-κB signaling that were identified as being significantly up- or down-regulated in the brain following TBI in Nlrx1−/− mice compared to the TBI wild type animals. Analysis was based on the ΔΔCt method, where all data was standardized to the average gene expression for a panel of 8 housekeeping genes and normalized to the respective non-lesion, contralateral region of each respective animal. Greater than a 2-fold change in gene expression was considered significant. Three randomly selected brains from each genotype and treatment group were selected and pooled for profiling studies. Pathway assessments were based on Ingenuity Pathway Analysis. (n=3 per group).