Figure 1. Reduced respiratory neural activity elicits rebound increases in phrenic burst amplitude.
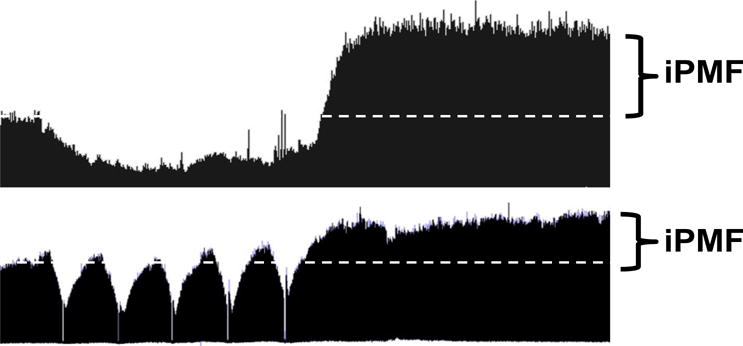
Compressed phrenic neurograms (~60 min recording) depicting baseline, a 30 min neural hypopnea (top) or 5, brief (~1 min) hypopneas separated by 5 min (bottom). Enhanced phrenic amplitude after neural hypopnea indicates iPMF.
