Fig. 2.
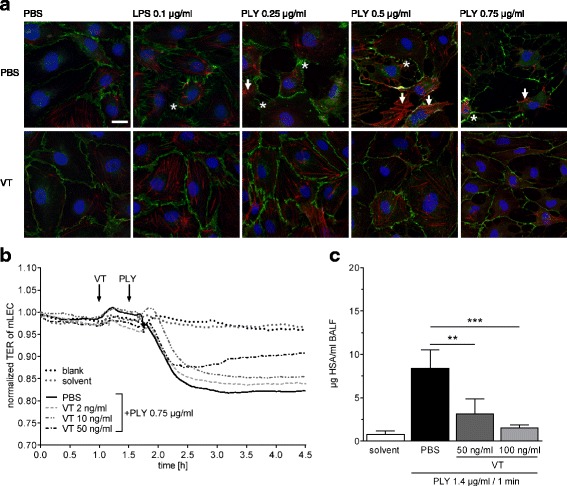
Vasculotide (VT) stabilized endothelial barrier function in vitro and ex vivo. a Confluent human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (hPMVEC) were preincubated for 90 minutes with 300 ng/ml VT or solvent (PBS) and stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS; 0.1 μg/ml), pneumolysin (PLY; 0.25, 0.5, or 0.75 μg/ml), or PBS for 30 minutes. Cells were fixed and vascular endothelial (VE)-cadherin (green), actin fibers (red), and cell nuclei (blue) were stained for immunofluorescence microscopy. Unstimulated, PBS-treated, or VT-treated cells showed intact monolayers with tight intercellular contacts and thin actin fibers (red). In PBS-pretreated groups, the integrity between cell contacts was disrupted, and hPMVEC showed gap formation (asterisks) and stress fibers (arrows) after LPS or PLY stimulation (upper row). Pretreatment with VT stabilized the cell monolayer, avoided gap formation, and reduced stress fibers and cell loss from culture dishes (lower row). Representative images of three independent experiments are shown for every group. a Bar = 20 μm (valid for all photomicrographs). b Transcellular electrical resistance (TER) of isolated murine lung endothelial cell (mLEC) monolayers was continuously monitored. mLEC were pretreated for 30 minutes with VT (2, 10, or 50 ng/ml) or PBS and then stimulated with pneumolysin (PLY; 0.75 μg/ml). PLY stimulation decreased TER of mLEC monolayers, displaying loss of endothelial integrity (solid curve). Preincubation with VT attenuated the PLY-induced TER decrease in a dose-dependent manner (dashed and dash-dotted curves). c Ex vivo perfused and ventilated mouse lungs were pretreated with VT (50 ng/ml or 100 ng/ml) or PBS 15 minutes before PLY stimulation (1.4 μg/ml). After 30 minutes, lung vascular permeability was assessed by quantifying the concentration of continuously infused human serum albumin (HSA) in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). Treatment with VT significantly decreased hyperpermeability of mouse lungs as compared with PBS treatment. Values are given as mean (C; n = 4–7) or mean + SEM (D; n = 6–8). **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 between indicated groups
