Fig. 1.
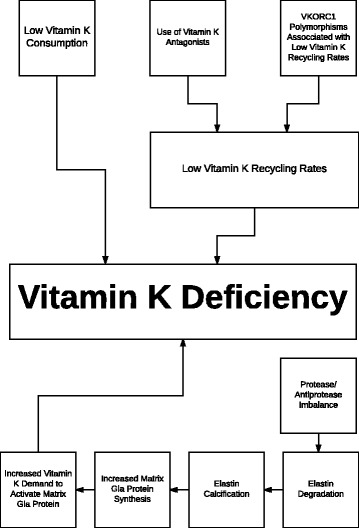
Proposed mechanisms that could be responsible for vitamin K deficiency. Low vitamin K consumption and use of vitamin K antagonists induce vitamin K deficiency. It is likely that polymorphisms in vitamin K epoxide reductase complex subunit 1 (VKORC1) gene associated with low vitamin K recycling rates predispose to vitamin K deficiency. Accelerated elastin degradation, due to a protease/antiprotease imbalance, leads to elastin calcification and subsequently to an increased synthesis of matrix Gla protein, which needs to be activated by vitamin K. This increased vitamin K demand might also cause a vitamin K deficit
