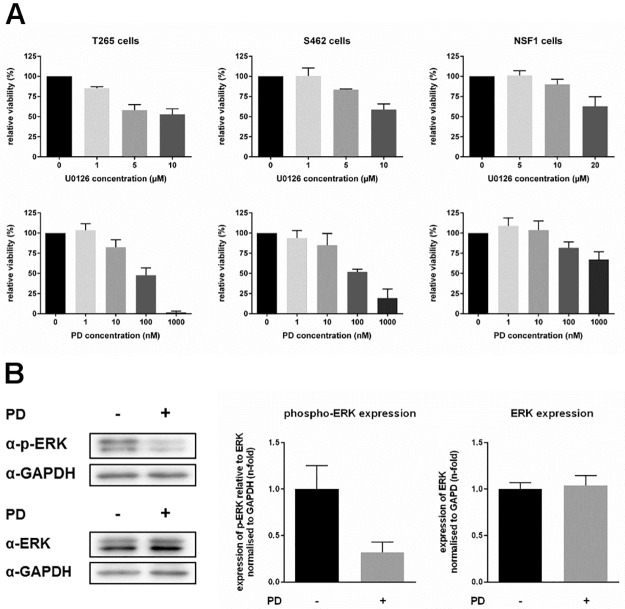
Fig 6. MEK inhibition reduces viability of MPNST cells.
Viability of MPNST cells under MEKi treatment was monitored by MTT. MPNST cells were treated with different doses of MEKi U0126 (upper panel) or PD0325901 (lower panel). T265 cells and S462 cells highly responded to MEKi treatment with reduced viability, whereas NSF1 cells did not show enhanced sensitivity to MEKi treatment, compared to untreated control cells (black bars). Maximum reduction of viability was achieved at 10 μM of U0126 and 1 μM of PD0325901 (reduction down to 53% ± 7% and 2% ± 1% in T265 cells, and 59% ± 7% and 19% ± 11% in S462 cells) (mean value of 3–5 measurements in each cell line (A). Relative ERK-P expression in T265 cells after MEKi treatment was analyzed. Western blots of ERK-P, ERK and GAPDH antibodies are demonstrated exemplarily for T265 cells after treatment with 10 nM PD0325901 (+) compared to untreated cells (-). T265 cells treated with MEKi demonstrated strongly reduced phosphorylated ERK level (grey bar, 0.32-fold ± 0.11-fold) compared to untreated control cells (black bar, 1.00-fold ± 0.25-fold). PD0325901 treatment did not affect total ERK level in treated (grey bar, 1.04-fold ± 0.07-fold) versus untreated T265 cells (black bar, 1.00-fold ± 0.11-fold) (mean value of 3 repeated measurements).