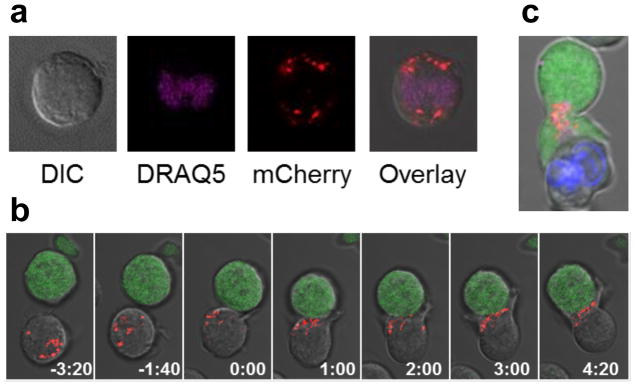
Figure 6.
Engineered GrB-mCherry molecules are efficiently expressed, packaged into lytic granules, and trafficked to the immunological synapse by human T cells. (a) Jurkat T cells nucleofected to express a GrB-mCherry fusion (red) and stained with the nuclear dye DRAQ5 (purple) display a punctate and cytoplasmic distribution of GrB-mCherry, consistent with the packaging and storage of wild-type GrB in lytic granules. (b) Time-lapse confocal microscopy of Jurkat T cells co-expressing a CD19 CAR and GrB-mCherry (red) reveals rapid movement of GrB-mCherry to the immunological synapse upon encounter with Raji target cells (green) that naturally expresses CD19. Time signatures indicate minutes:seconds, with 0:00 set to the time of initial cell-cell contact. (c) Jurkat T cells co-expressing CD19 CAR and GrB-mCherry (red) were pre-loaded with the calcium indicator Fluo-4 and co-incubated with CD19+ Raji cells pre-labeled by Hoechst 33342 staining (blue). Fluo-4 signal (green) indicates T-cell activation triggered by target-cell engagement, which was accompanied by rapid and sustained GrB-mCherry polarization to the immunological synapse in preparation for directional release toward the target cell.