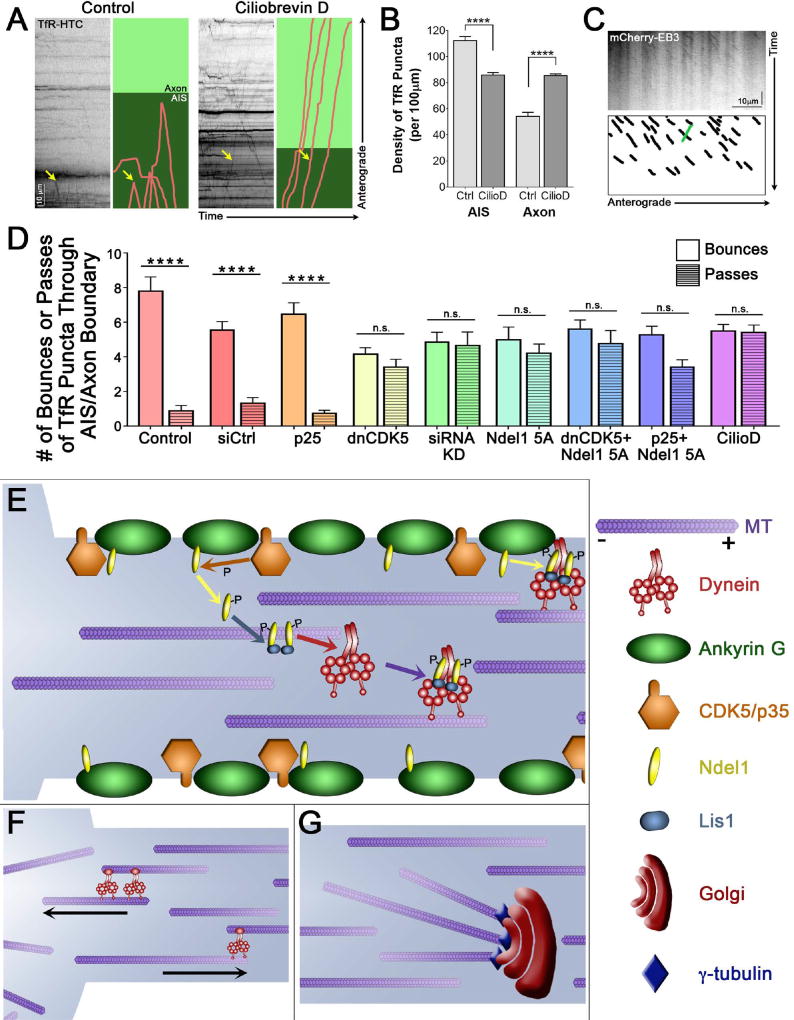
Figure 7. CDK5 differentially disrupts somatodendritic cargo trafficking and microtubule polarity in a temporally specific manner, and regulates dynein activation and axonal microtubule polarity.
(A) Kymographs of TfR motion in 7 DIV rat hippocampal neurons in the presence of the dynein inhibitor ciliobrevin D. Individual runs highlighted to the right: runs shown in pink, axon in light green and AIS, as determined by co-expression of NaV II–III, in dark green. Yellow arrow marks the same run on both the kymograph and the cartoon.
(B) Quantification of the density of TfR puncta in the AIS or the axon with short-term dynein inhibition with ciliobrevin D in 7 DIV rat hippocampal neurons as in (A).
(C) Kymograph of EB3 motion in the axons of 7 DIV rat hippocampal neurons expressing mCherry-EB3 after 1.5–3 hours of dynein inhibition with ciliobrevin D. Schematic below highlights all anterograde-directed EB3 comets in axons (black), and any visible retrograde-directed EB3 comets (one, green).
(D) Quantification of the percent of TfR puncta rebounding from and passing through the AIS/axon boundary with expression and exposure to various CDK5 and dynein activators and inhibitors in 7 DIV rat hippocampal neurons (from Figures 4–5, 7).
(E) AnkG (green) and CDK5/p35 (orange) localize to the neuronal membrane in the AIS. Ndel1 (yellow) binds to AnkG at the membrane, until phosphorylation by CDK5 causes it to release. Phosphorylated Ndel1 binds to Lis1 (blue) in a 2:2 ratio, which then recruits dynein (red). The Ndel1/Lis1/dynein complex engages the microtubule (purple), initiating retrograde-directed axonal transport. This activation can also occur at the membrane, activating cortical dynein.
(F) Axonal microtubules are uniformly oriented with their plus-ends out, while microtubules in the soma are regulated differently. Minus-end-out microtubules that enter the axon from the soma are returned to the soma by the actions of dynein attached to correctly polarized microtubules. Plus-end-out microtubules that enter the axon are propelled forward and permitted to stay in the axon.
(G) Golgi bodies (burgundy) contain γ-tubulin (indigo) at the cis-Golgi membrane. The minus-end of microtubules are stabilized through interactions with the γ-tubulin at the axonal Golgi bodies.
Scale bar represents 10µm and 10 seconds (A) or 30 seconds (C). Graphs depict means ± SEM; n ≥ 20 neurons from at least three biological replicates. Values that differ significantly (one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test) are noted on graphs (****p < 0.0001).