Figure 6.
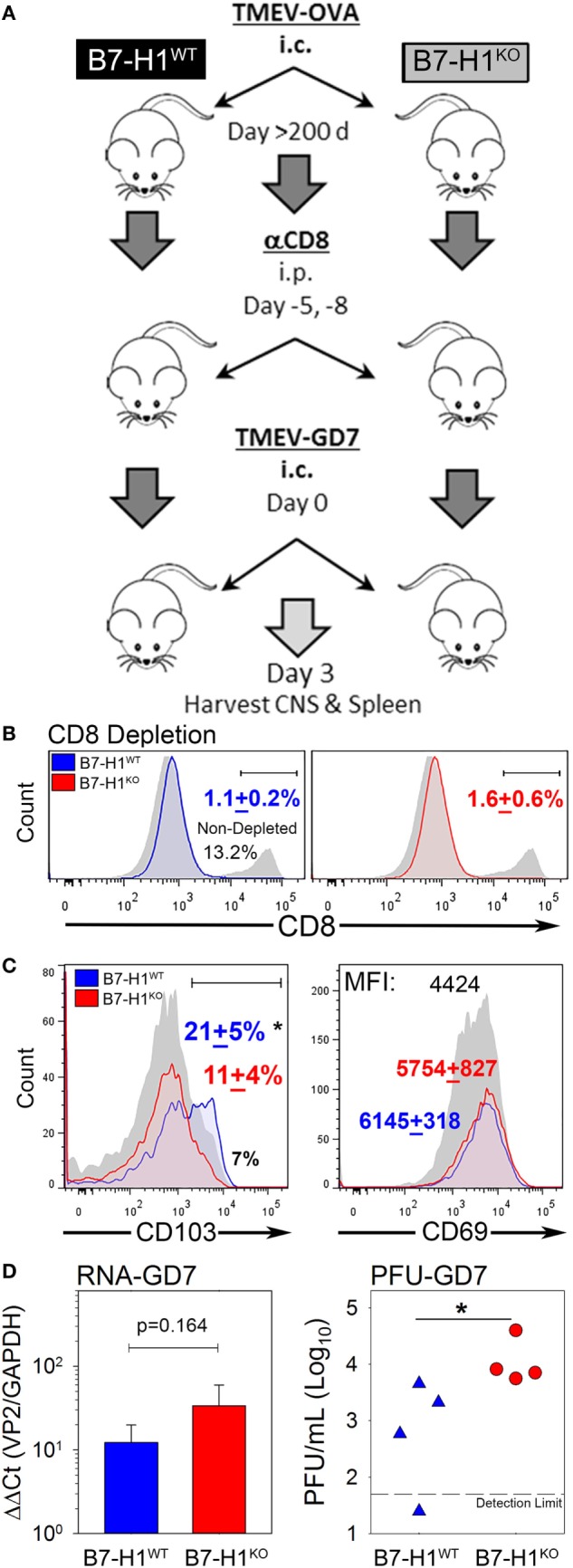
B7-H1 promotes tissue resident memory CD8+ T-cell protection from heterologous secondary infection. (A) Virus re-challenge scheme to determine the role of B7-H1 in protecting mice from a secondary tissue-specific re-challenge with the Theiler’s murine encephalomyelitis virus (TMEV) variant GD7. (B) Splenocytes were analyzed for CD8 expression in B7-H1WT and B7-H1KO mice depleted with CD8 depleting antibody for verify depletion of peripheral CD8+ T-cells. Splenocytes were gated on forward-side scatter and CD45 subsequent to analysis of the percent of CD8+ cells (n = 4 per group). One non-CD8 depleted animal infected with TMEV-OVA8 is used as a reference to determine relative depletion (gray/black). (C) CD103 and CD69 expression on CD8+ T-cells recovered from the CNS on day 3 after TMEV-GD7 re-challenge. (D) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis for TMEV-GD7 specific transcripts from the CNS of B7-H1WT and B7-H1KO mice given a re-challenge with TMEV-GD7. (Right) Plaque assay performed on CNS homogenates recovered from re-infected B7-H1WT and B7-H1KO mice (PFU, plaque-forming units). *Significant by t-test p < 0.05; B7-H1WT versus B7-H1KO.
