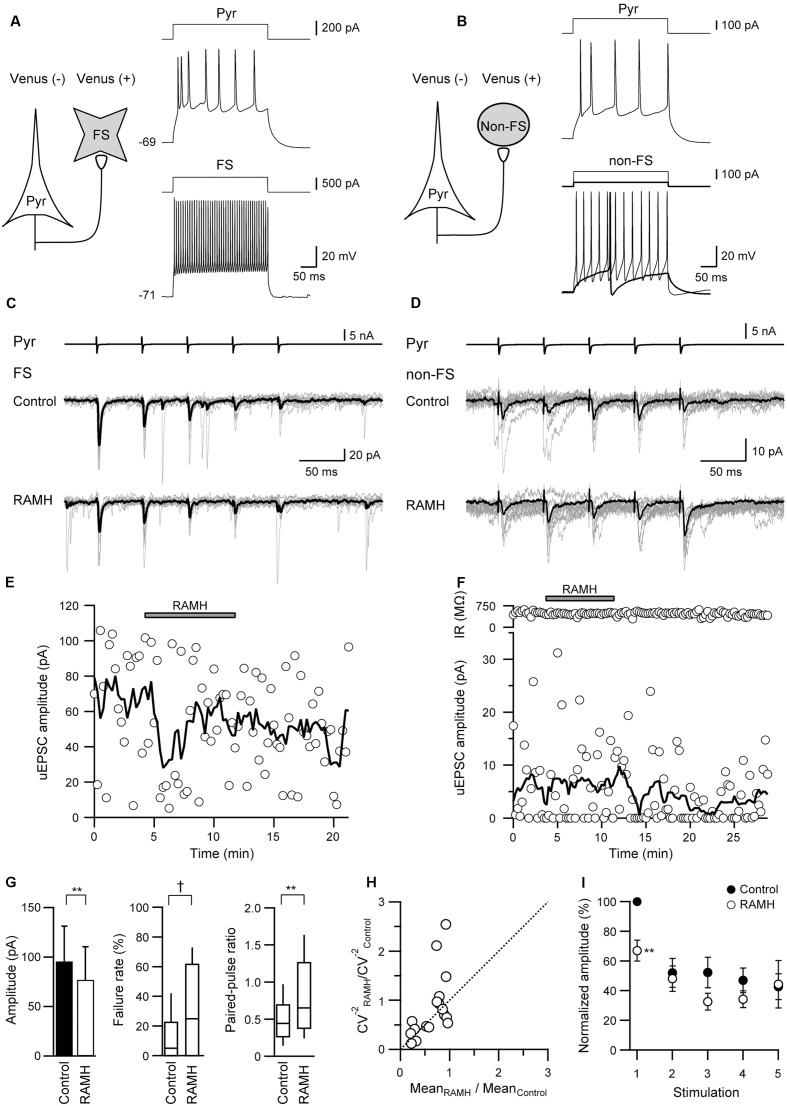
FIGURE 2.
The effects of 10 μM RAMH on uEPSCs in pyramidal cell to fast-spiking (FS) or non-fast-spiking neuron (non-FS; Pyr→FS/non-FS) connections. (A,B) Schemes of a Pyr→FS (A) and a Pyr→non-FS connection (B) with suprathreshold voltage responses of each neuron. (C,D) uEPSC recordings from the Pyr→FS (C) and the Pyr→non-FS (D) connections responding to an injection of five short train pulses to the pyramidal cells (2 ms, +80 mV, 20 Hz; upper traces) shown in (A,B), respectively (Vh = –70 mV). Eleven consecutive traces (gray) and their average traces (black) are shown. Note that the uEPSC amplitude was reduced after RAMH application in both connections. (E,F) Time courses of the uEPSC amplitude before, during, and after RAMH application in Pyr→FS (E) and Pyr→non-FS connections (F). Input resistance (IR) was shown in (F). (G) RAMH-induced effects on the uEPSC amplitude, failure rate, and paired-pulse ratio in Pyr→FS/non-FS connections (n = 18). (H) CV analysis in Pyr→FS/non-FS connections. (I) The normalized amplitude of the 1st to 5th uEPSCs (n = 18). Filled and open circles indicate the normalized amplitude of uEPSCs in control and during RAMH application, respectively. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, paired t-test. †P < 0.05, Wilcoxon test.