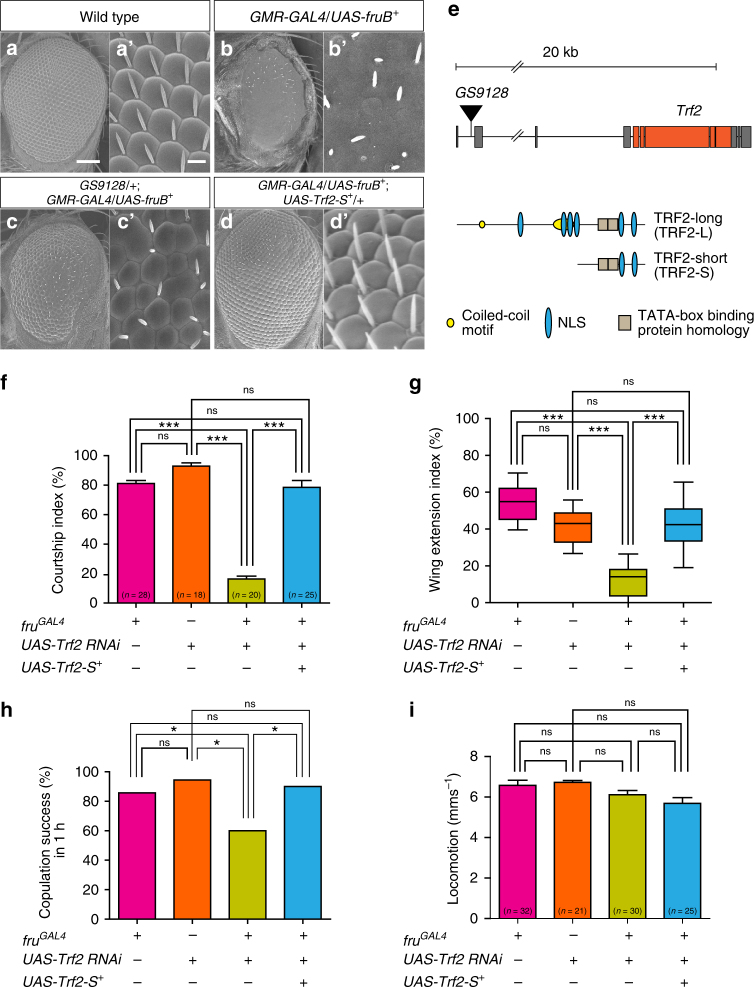
Fig. 1.
Phenotypic interactions of Trf2 and fru. a–d A regular array of ommatidia in the compound eye (wild type: a) was distorted by fruB + overexpression (b), and the fruB +-induced eye phenotype was partially rescued by GS9128 (c) or Trf2-S + overexpression (d). Enlarged views are shown in a′–d′. e Schematic drawings of the genomic organization of the Trf2 locus with the GS9128 P-insertion (upper panel) and TRF2-L and TRF2-S isoforms (lower panel). f–i Trf2-S knockdown in fru GAL4-expressing cells reduced the courtship index (f), wing extension index (g), and copulation success (h), but had no effect on locomotor activity (i) in male flies, and the effects of Trf2 knockdown were compensated by Trf2-S + overexpression (f–h). Statistical differences were evaluated by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test (f, i), by the Kruskal–Wallis test followed by the Dunn’s multiple comparison test (g), or by the χ 2-test (h). ***P < 0.001, *P < 0.05; ns not significant. The number of flies examined is indicated near the base of each bar. Data shown in f–h were obtained from the same fly group, whereas data shown in i were derived from a fly group different from that used in f–h. Error bars indicate SEM. Scale bars: 200 µm (a), 30 µm (a′)