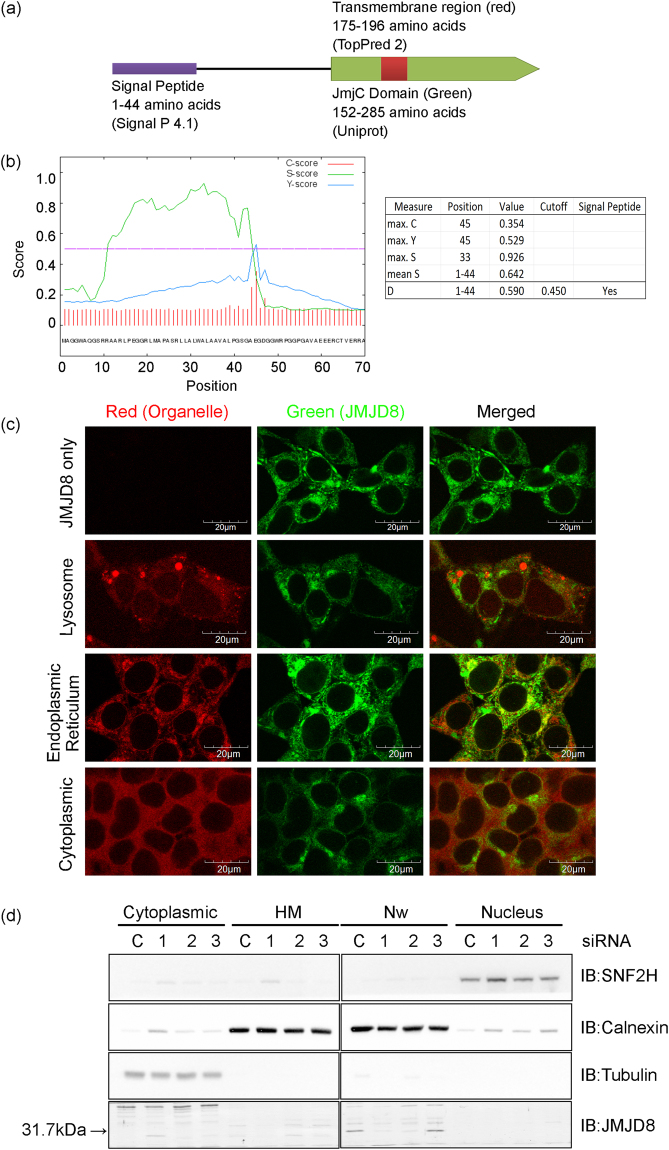
Figure 1.
JMJD8 is an ER protein. (a) Schematic structure of JMJD8 predicted using indicated bioinformatics tools. (b) The protein sequence of JMJD8 obtained from NCBI was subjected to SignalP 4.1 analysis and three different scores were measured. The raw cleavage site score (C-score) is the output of the cleavage site prediction network, which is trained to distinguish signal peptide cleavage site; signal peptide score (S-score) is the output of signal peptide prediction network, which is trained to locate the signal peptides of a protein; and Y-score is a combination of C-score and the slope of S-score. In addition, mean S represented the average S-score of the possible signal peptide, whereas discrimination score (D-score) represented the mean S and maximum Y scores, which is used to discriminate signal peptide from the non-signal peptide. (c) HEK293T-JMJD8-eCFP stable cells were stained with LysoTracker (Lysosome), ER-tracker (Endoplasmic reticulum) or an anti-p65 antibody (Cytoplasmic). The yellow staining in the overlay image indicates colocalization of JMJD8 with ER. Images were acquired with an Olympus FV1000 confocal microscope. Scale bar: 20 μm. (n = 3). (d) HEK293T cells were transfected with either 10 nM control or an siRNA targeting JMJD8. Three siRNA oligos were tested to facilitate the identification of endogenous JMJD8 by immunoblotting. Cell lysates were prepared and fractionated into cytoplasmic, heavy membrane (HM-rich in lysosomes, ER, and mitochondria), nuclear wash (Nw-rich in ER) and nuclear fractions. The organelle specific proteins and JMJD8 were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies (Nuclear with SNF2h, ER with calnexin and cytoplasmic with tubulin). (n = 3). Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Fig. S5.