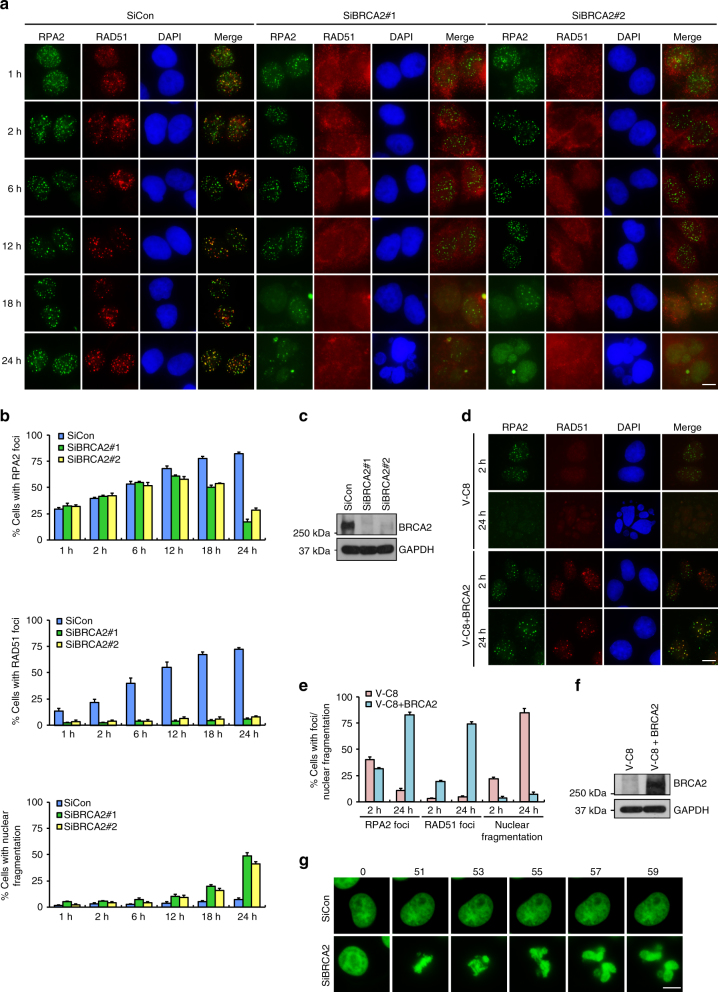
Fig. 1.
BRCA2 depletion accelerates the dissolution of RPA2 foci and causes massive nuclear fragmentation. a HeLa cells were transfected with control siRNA or siRNAs against BRCA2. Forty-eight hours post transfection, cells were exposed to 10 Gy IR and then allowed to recover for the indicated time periods before being processed for immunofluorescence using antibodies against RPA2 and RAD51. Representative RPA2/RAD51 foci and DAPI-stained nuclei are shown. b Quantification of RPA2/RAD51 foci and nuclear fragmentation. Data represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Over 100 cells were counted in each experiment. c Knockdown efficiency of BRCA2 was confirmed by western blotting. d BRCA2-deficient VC-8 cells or VC-8 cells reconstituted with wild-type BRCA2 were exposed to 10 Gy IR and then allowed to recover for 2 or 24 h before being processed for immunofluorescence using antibodies against RPA2 and RAD51. Representative RPA2/RAD51 foci and DAPI-stained nuclei are shown. e Quantification of RPA2/RAD51 foci and nuclear fragmentation. Data represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Over 100 cells were counted in each experiment. f Expression of BRCA2 was confirmed by western blotting. g HeLa cells stably expressing GFP-tagged histone H2B (H2B-GFP) were transfected with control siRNA or siRNA against BRCA2. Forty-eight hours post transfection, cells were exposed to 10 Gy IR. Arbitrary cells were selected between 16 and 24 h after IR and performed to visualize chromosomal dynamics by time-lapse imaging (5 min per frame, 0 = 16 h, 51 = 20.25 h). Scale bars, 10 μm