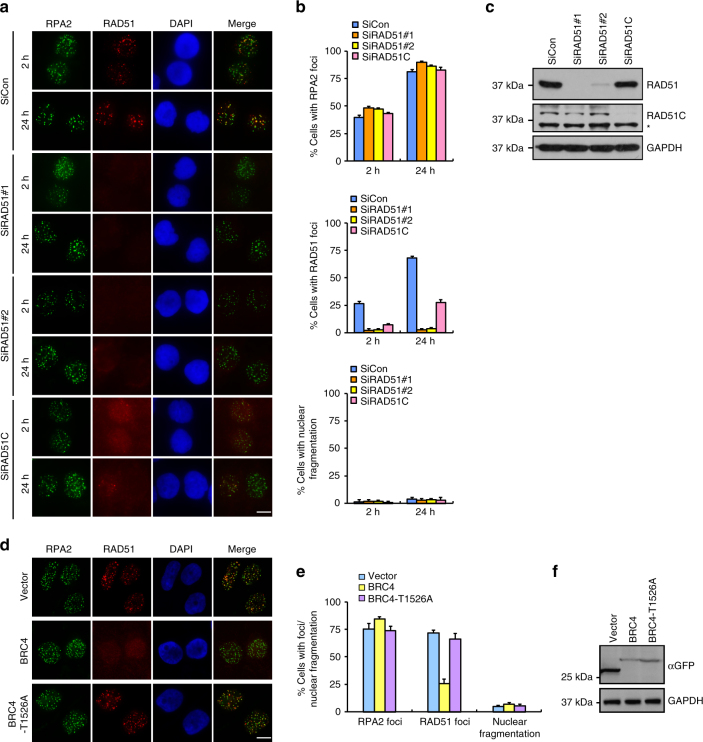
Fig. 2.
BRCA2 suppresses gross genomic instability independently of RAD51. a HeLa cells were transfected with control siRNA or siRNAs against RAD51 or RAD51C. Forty-eight hours post transfection, cells were exposed to 10 Gy IR and then allowed to recover for 2 or 24 h before being processed for immunofluorescence using antibodies against RPA2 and RAD51. Representative RPA2/RAD51 foci and DAPI-stained nuclei are shown. b Quantification of RPA2/RAD51 foci and nuclear fragmentation. Data represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Over 100 cells were counted in each experiment. c Knockdown efficiency of RAD51/RAD51C was confirmed by western blotting. The asterisk indicates a nonspecific band. d HeLa cells were electroporated with GFP-tagged wild-type BRC4 or the T1526A mutant. Twenty-four hours later, cells were exposed to 10 Gy IR and then allowed to recover for 24 h before being processed for immunofluorescence using antibodies against RPA2 and RAD51. Representative RPA2/RAD51 foci and DAPI-stained nuclei are shown. e Quantification of RPA2/RAD51 foci and nuclear fragmentation. Data represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Over 100 cells were counted in each experiment. f BRC4 expression was confirmed by western blotting. Scale bars, 10 μm