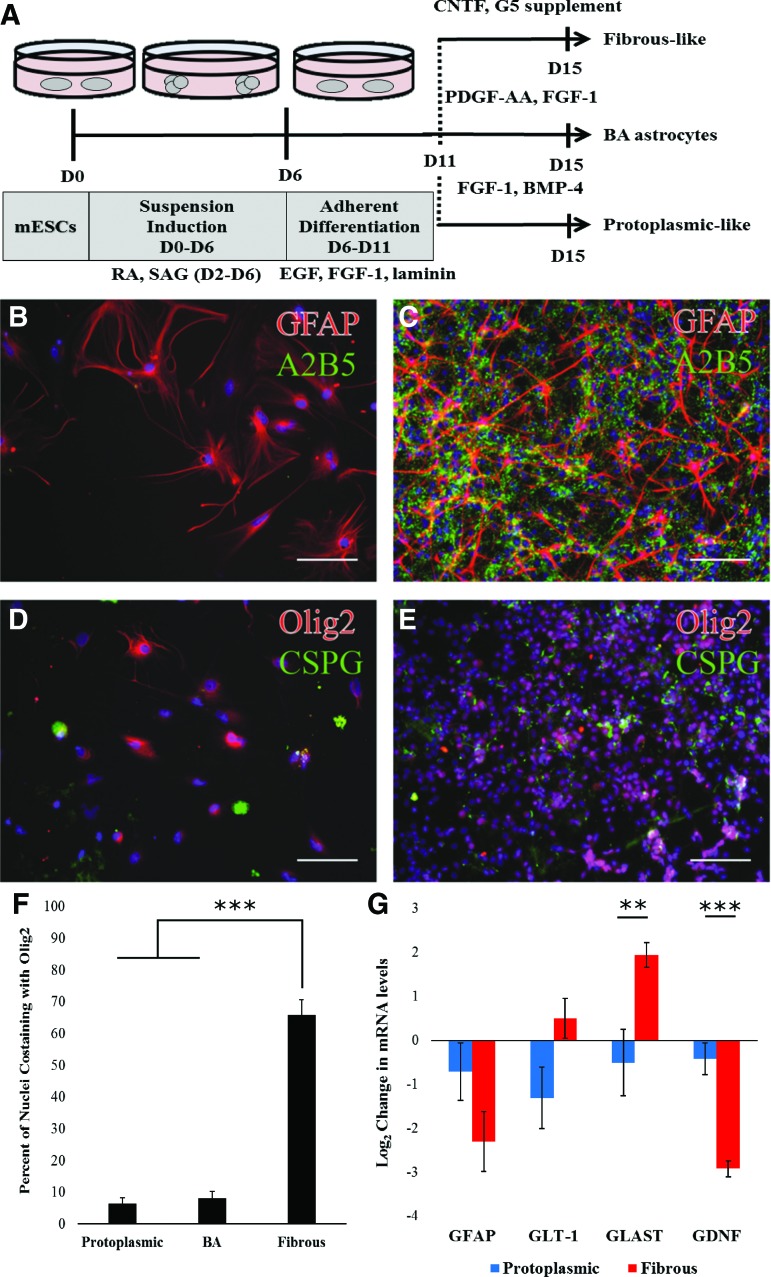
FIG. 1.
mESCs can be selectively differentiated into mixed populations containing either protoplasmic or fibrous astrocytes. (A) Schematic representation of the astrocyte differentiation protocols used in this work. All astrocytes are subjected to the same initial 11 days after which media factors are changed so that fibrous, protoplasmic, or the BA (Benveniste protocol [18]) population develops. (B, C) GFAP (red) and A2B5 (green) staining in protoplasmic (B) or fibrous (C) cultures at the end of differentiation. (D, E) Olig2 (red) and CSPG (green) staining in protoplasmic (D) or fibrous cultures (E) at end of differentiation. Nuclei stained with Hoechst (blue). Scale bar: 100 μm. (F) Quantification showing the percent of nuclei that colocalized with Olig2 staining in different cultures. Error bars: standard error, n = 9–12. (G) Log2 expression difference in mRNA levels for fibrous and protoplasmic astrocyte markers compared to BA control population. Error bars represent standard error, n = 6. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. BMP-4, bone morphogenetic protein 4; CNTF, ciliary neurotrophic factor; CSPG, chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan; EGF, epithelial growth factor; FGF-1, fibroblast growth factor 1; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; mESC, mouse embryonic stem cells; PDGF-AA, platelet-derived growth factor AA; RA, retinoic acid; SAG, smoothened agonist. Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/scd