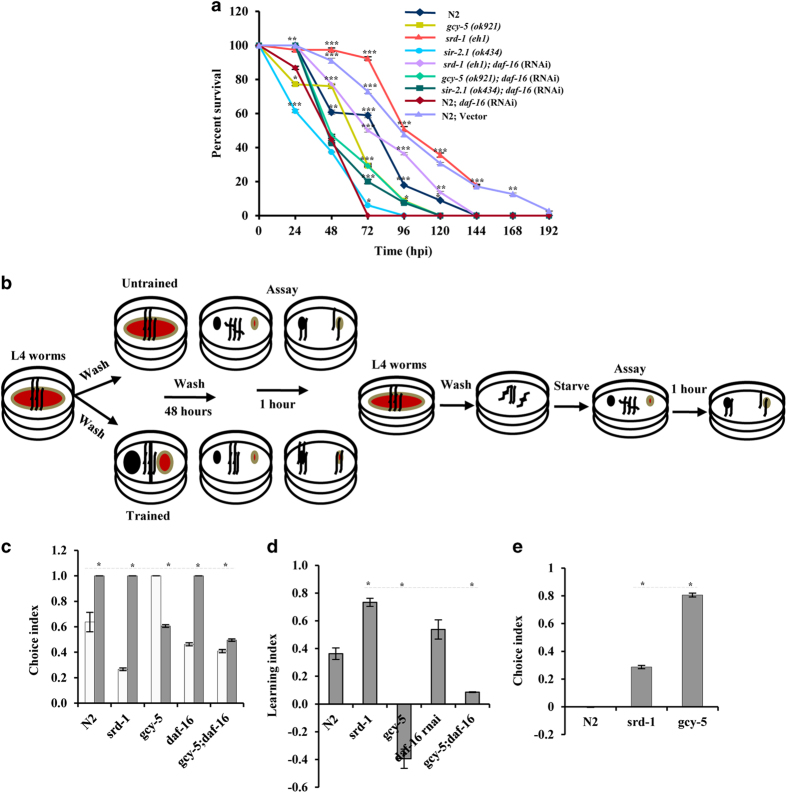
Figure 6.
Influence of DAF-16 on neuronal and non-neuronal genes and aversion assay for studying pathogen avoidance in C. elegans. (a) Wild-type daf-16 RNAi, gcy-5, srd-1, sir-2.1 mutants, gcy-5; daf-16 RNAi, srd-1; daf-16 RNAi, and sir-2.1; daf-16 RNAi were infected with F. oxysporum under non-avoidance conditions. N=50 adult animals for each strain. Error bars represent S.E. from three independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, and ***P<0.001 by one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post hoc test. P-values are relative to N2; daf-16 (RNAi) worms. (b) A schematic representation of the assays developed for understanding the behavioural response to F. oxysporum in C. elegans. (c) Choice index of wild-type srd-1, gcy-5, daf-16, and gcy-5;daf-16 worms. The white bar represents the choice index for E. coli OP50 and the coloured bar represents the choice index for F. oxysporum. (d) Learning index of wild-type srd-1, gcy-5, daf-16, and gcy-5;daf-16 worms. (e) Normalised choice index of wild-type srd-1 and gcy-5 worms. N=30 adult animals for each strain. Error bars represent S.E. from three independent experiments. *P<0.05, t test with Bonferroni correction.