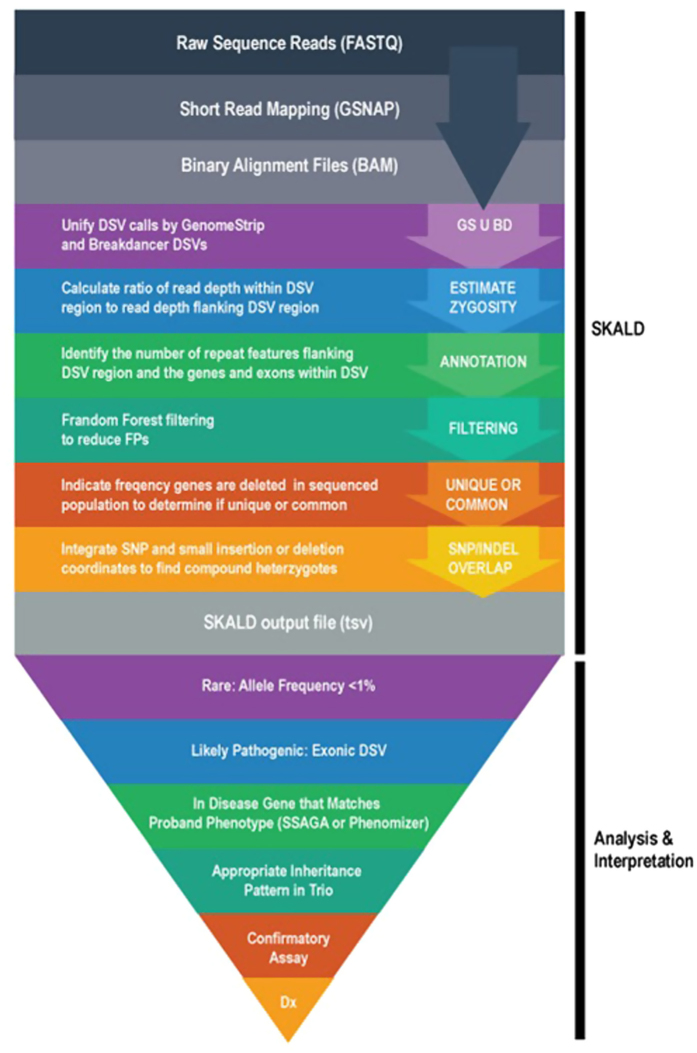
Figure 3.
A flow diagram of the SKALD pipeline and downstream analysis for detection of likely disease-causative DSVs in WGS. After reads were aligned, GS and BD were executed concurrently on bam files from parent–child trios. Filter attributes, overlap % and annotations were obtained for each BD U GS DSV prediction. Since genes that were commonly deleted were unlikely to be deleterious, the population frequency of DSVs overlapping genes helped determine whether the DSV was likely to cause a rare genetic disease. Finally to identify likely pathogenic compound heterozygote states, any SNVs or indels overlapping a DSV were included as part of the SKALD output in the form of a tab separated text file.