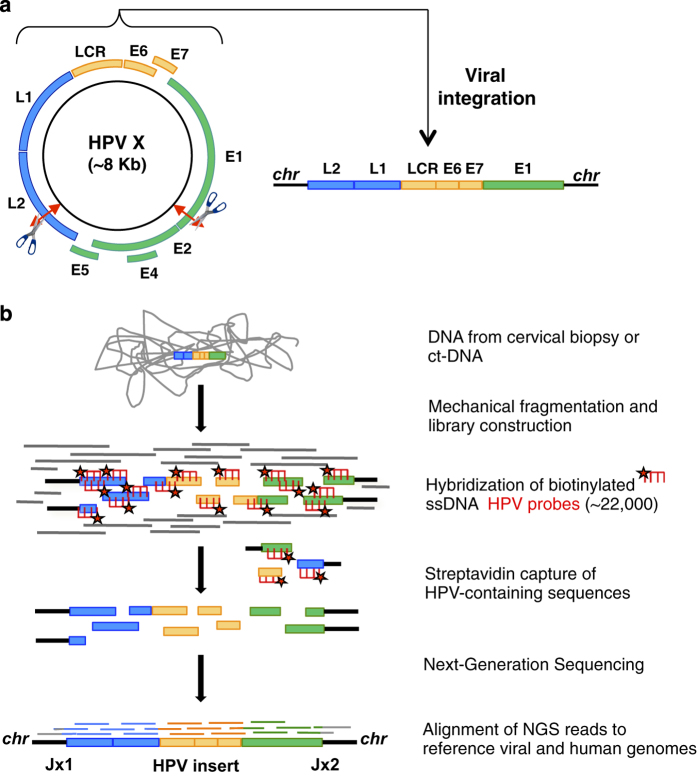
Figure 1.
Capture-NGS method to identify HPV genotypes and integration sites. (a) The HPV dsDNA circular genome contains early (E) and late (L) replicating genes, necessary for viral replication and capsid formation. Integration and disruption/loss of the E2 suppressor gene sequences may lead to overexpression of the E6 and E7 viral oncogenic sequences, as well as disruption of host genomic DNA sequences. (b) Capture-NGS of HPV-integrated viral–cellular junctions. Genomic DNA is mechanically and homogeneously nebulised, followed by dsDNA library preparation and annealing of adaptor barcodes. HPV-biotinylated single-stranded probes (~22,000) then bind and capture HPV-containing library sequences that are enriched on a streptavidin column. These enriched DNA products are sequenced by NGS whose read alignments permit identification of the genotype, as well as the HPV-cellular hybrid junctions and localisation of the HPV insert in the tumour genome.