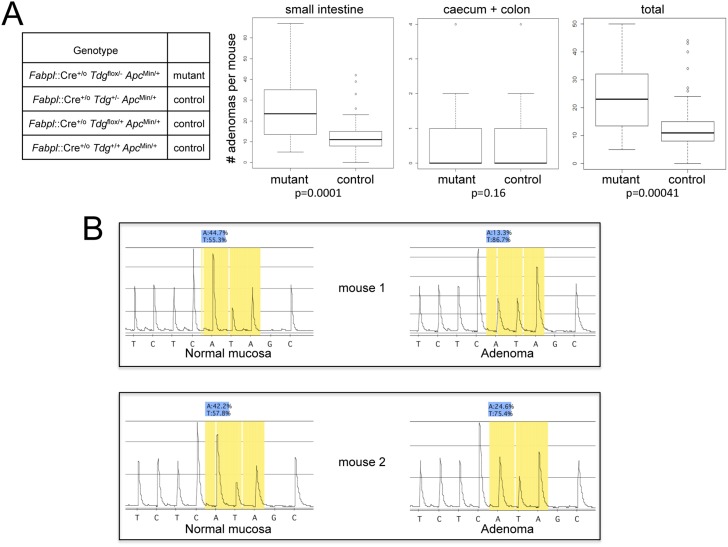
Figure 1. Increased intestinal tumor formation in Tdg conditional knock-out mice crossed into the ApcMin background.
(A) Box plot representation of the distributional characteristics of the number of small intestinal, caecum plus colonic, and total adenomas in experimental Fabpl::Cre+/o Tdgflox/- ApcMin/+ (mutant) and Fabpl::Cre+/o Tdg+/- ApcMin/+, Fabpl::Cre+/o Tdg+/flox ApcMin/+ and Fabpl::Cre+/o Tdg+/+ ApcMin/+ (control) mice; the line in the box represents the median. The p value was determined by two-sided Mann-Whitney test. The average tumor numbers and standard deviations are as follows: small intestinal, mutant: mean=26, SD=15.68; small intestinal, control: mean=12.76, SD=8.95; colon, mutant: mean=0.84, SD=1.26; colon, control: mean=0.41, SD=0.74; total, mutant: mean=23.84, SD=12.70; total, control: mean=13.16, SD=9.35. (B) Pyrogram of the complementary sequence around the ApcMin mutation showing evidence of loss of heterozygosity in two adenomas from Fabpl::Cre+/o Tdgflox/- ApcMin/+ mice in comparison to normal mucosa. The ApcMin mutation, a T→A point mutation at base 2,549, is present in heterozygosity (approximately 50%) in normal mucosa of Fabpl::Cre+/o Tdgflox/- ApcMin/+ mice, and increases to approximately 75-85% in adenomas.