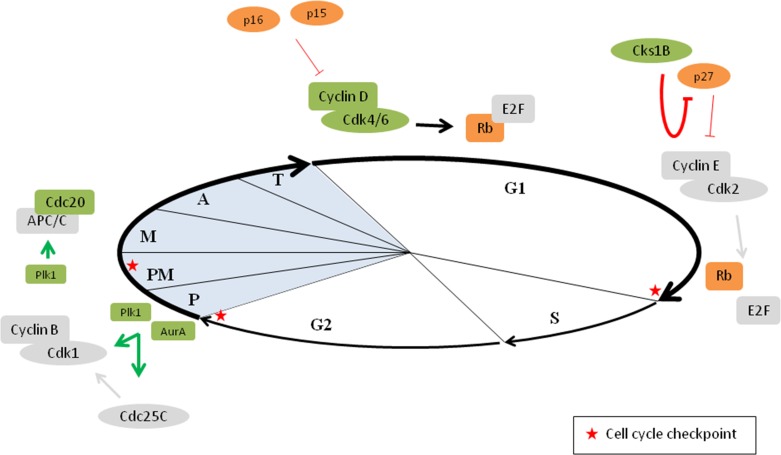
Figure 3. Deregulation of the cell cycle in multiple myeloma.
Defects in cell cycle progression is a common feature in cancer cells. In multiple myeloma, cyclin D overexpression is observed in virtually all MGUS and MM patients. In addition, overexpression of Cdk4/6, loss of the INK4 family inhibitors and loss of Rb protein is also frequently observed. Together these events result in more E2F release and hence progression through the G1/S restriction point. Cks1B overexpression is inversely linked to p27 expression, which promotes the G1/S transition. In addition, Aurora A kinase (AurA) and polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) levels are also frequently increased in MM cells, resulting in increased activation of cyclin B–Cdk1 complexes. Finally, Plk1 and Cdc20 proteins are also overexpressed in MM cells leading to more APC/C activation. Proteins depicted in orange are decreased in MM, proteins depicted in green are increased in MM, P: prophase, PM: prometaphase, M: metaphase, A: anaphase and T: telophase.