Figure 1. AD‐related neurodegeneration and HF‐HRV.
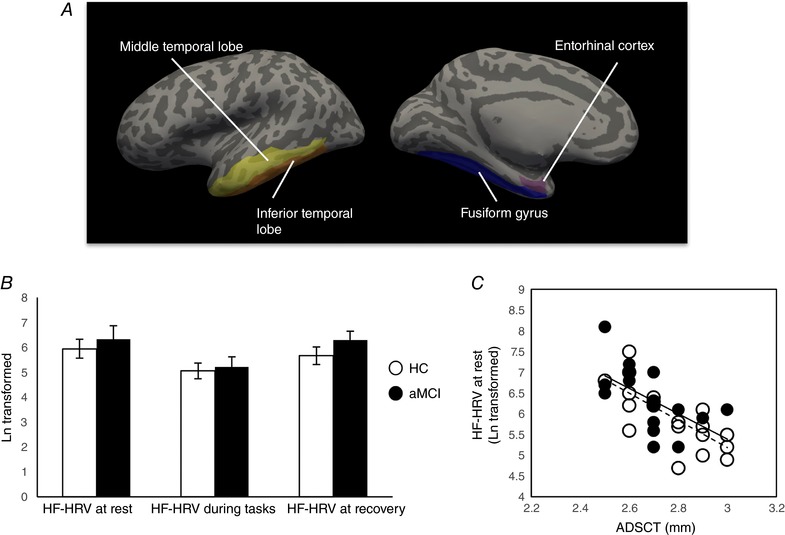
A, AD‐related neurodegeneration was indexed by ADSCT, which was defined by averaging cortical thickness of bilateral inferior and middle temporal lobes, entorhinal cortex and fusiform gyrus. Here, lower value indicated more severe AD pathology. B, mean and SEM of HF‐HRV at rest, during tasks and at recovery by group. There was a significant quadratic pattern for HF‐HRV (i.e. declined from at rest to tasks, and rebounded after recovery) in both groups, but there was no group by status interaction effect. C, there was a significant association between ADSCT and HF‐HRV at rest but not HF‐HRV reactivity (calculated as the difference between HF‐HRV at tasks and rest) controlled for age and sex. The dashed line represents the correlation in HC group, and the continuous line represents the correlation in aMCI group. Similarity is observed relationships for the two groups. [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
