Figure 5. TRPV4 stimulation rapidly and dramatically decreases the impedance of HrMVEC monolayers and increases the in vivo permeability of retinal blood vessels.
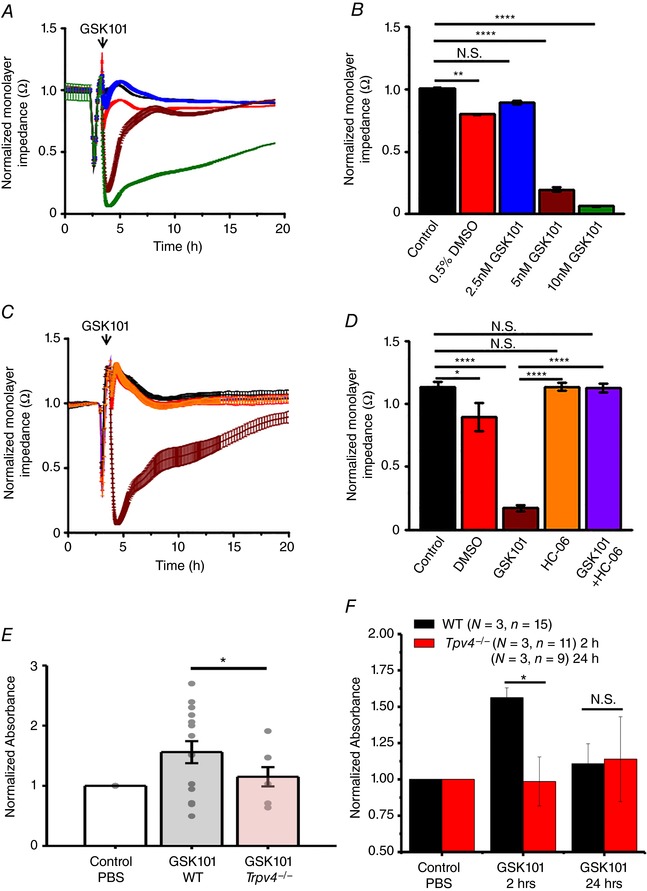
The ‘normalized monolayer impedance’ is derived by dividing the impedance value by the value at a reference time point. A, 2.5 nm (red), 5 nm (brown) and 10 nm (green trace) GSK101 dose‐dependently decrease the resistance of HrMVEC monolayers. B, cumulative data for the experiments shown in A (N = 3). C, HC‐06 (orange) inhibits 10 nm GSK101‐induced decreases in monolayer resistance (brown trace) (N = 3). D, averaged data from C. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.00001, paired t test. E, systemic injection of GSK101 increases the retinal extravasation of Evans Blue 2 h after dye injection, indicated by increased absorbance signal in WT (grey bar) compared to Trpv4−/− retinas (red bar). The dots represent individual retinas; values are normalized to control values of dye‐exposed retinas in the absence of the TRPV4 agonist. Retinal extravasation was measured 2 and 24 h after GSK101 treatment. F, cumulative data for three independent experiments from WT (black bars) and Trpv4−/− retinas measured 2 and 24 h after GSK101 treatment. * P = 0.033; N.S., P > 0.05; one‐way ANOVA. Mean ± SEM. [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
