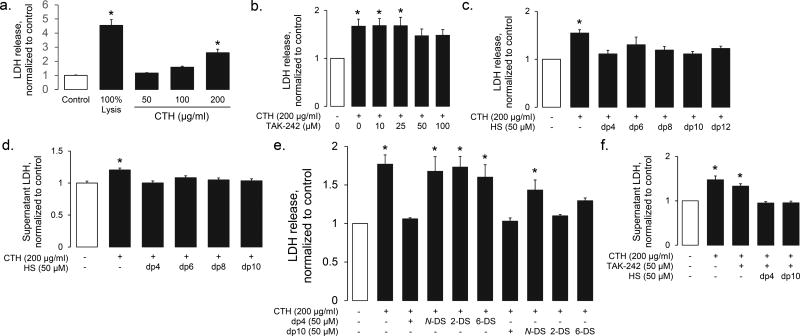
Figure 6. HS oligosaccharides prevent CTH-induced endothelial cytotoxicity.
(a) CTH induce endothelial cell death (as quantified by LDH release from HPMEC-ST1.6R endothelial cells) in a dose-dependent fashion. (b) CTH-induced endothelial (HPMEC-ST1.6R) cytotoxicity is minimally TLR-4 dependent, as demonstrated by only modest protection provided by high-dose TAK-242 (a TLR4 inhibitor). In contrast, HS oligosaccharides (of all sizes) protected against CTH-induced cytotoxicity in HPMEC-ST1.6R cells (c) and primary human lung microvascular endothelial cells (d). (e) The HPMEC-ST1.6R-protective effects of dp4 HS was dependent on N-, 2-O, and 6-O sulfation, while the protective effects of dp10 HS only required N-sulfation. (f) The protective effects of dp4 and dp10 HS were additive to (and therefore likely independent of) high-dose TLR4 inhibition. n > 3 independent replicates for all groups. * P < 0.05 compared to control group.