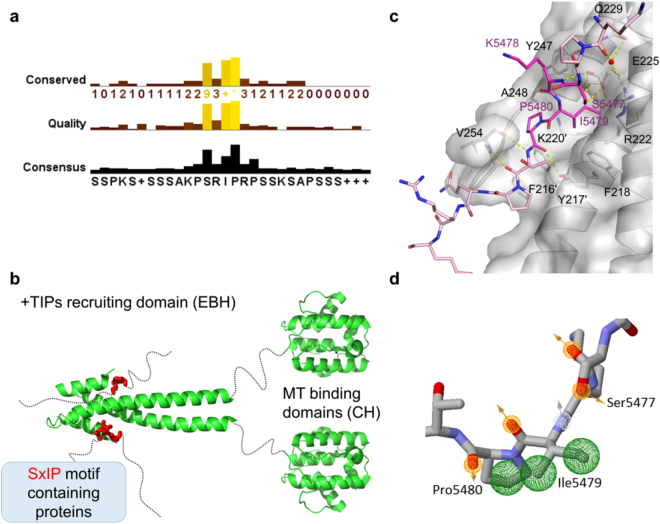
Figure 1.
(a) Conservation analysis for known SxIP proteins based on a 30 residue sequence encompassing the identified SxIP motif. Figure was made using JalView 2.8.2. (b) Model for the mechanism of the recruitment of the SxIP motif containing proteins by EB1. Both EB1 domains are shown in green – the microtubule binding domain – calponin homology (CH) domain and the + TIPs recruitment domain – EBH domain. The SxIP motif is shown as red sticks within a disordered region represented by a dashed line. There are more than 42 proteins known to bind to EB1 via this conserved motif. (c) Representation of the SxIP crystallographic binding mode as shown by Honnappa et al.5 SxIP containing peptide is shown as light pink sticks, and the SxIP motif is highlighted as bright pink sticks. EB1 is shown as cartoon and surface representations with important residues shown as sticks. (d) Representation of the pharmacophore points found for Ser5477, Ile5479 and Pro5480 of the MACFp1 peptide. All pharmacophore features are shown as spheres, with the hydrogen bonding acceptors showed as orange mesh, hydrogen bonding acceptors in white mesh and hydrophobic as green mesh. Orange and grey arrows indicate the direction of the hydrogen bond donor/acceptor, respectively.