FIGURE 5.
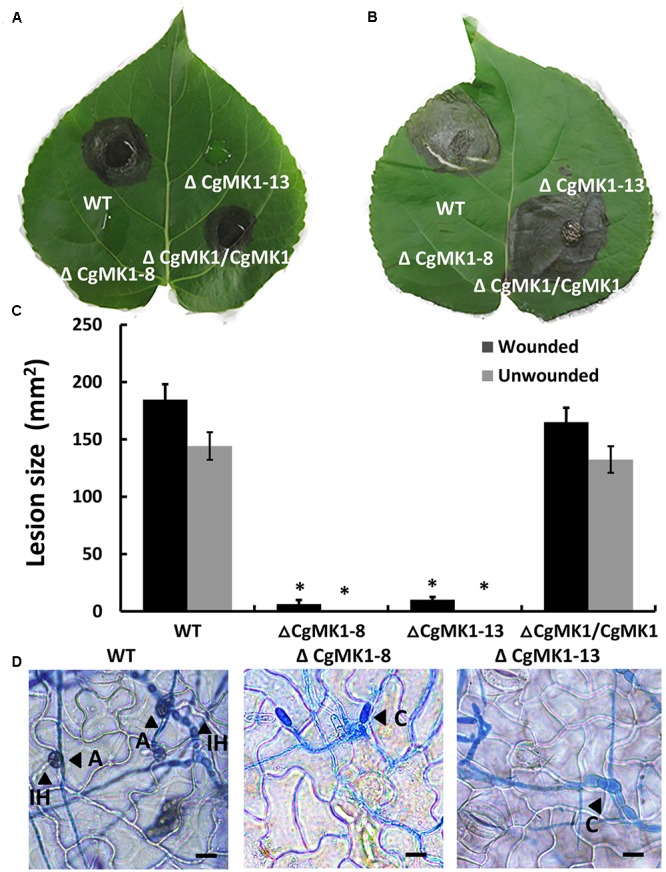
The CgMK1 deletion mutants lose pathogenicity on poplar leaves, indicating that CgMK1 governs virulence. (A) Spores (105/mL) from WT, ΔCgMK1 mutants and the ΔCgMK1/CgMK1 were inoculated on the detached leaves of 1-year-old poplar seedlings. Ten healthy intact poplar leaves were used in each independent experiment with three replicates. The images were captured at 7 dpi. (B) Spores (105/mL) of WT, ΔCgMK1 mutants and the ΔCgMK1/CgMK1 were inoculated on detached leaves of 1-year-old poplar seedlings. Ten poplar leaves were wounded and were used in each independent experiment with three replicates. The images were captured at 7 dpi. (C) Quantification of lesion sizes caused by the strains in each independent experiment. Values represent the mean of three repetitions. The data were performed by using the Duncan’s range test. Asterisks mean statistically significant differences at P = 0.05. (D) Infection hyphae development of the strains on the detached poplar leaves at 48 hpi. Invasive hyphae were treated with lactophenol aniline blue. A: appressorium; C: conidium; IH: invasive hyphae. Scale bar: 10 μm.
