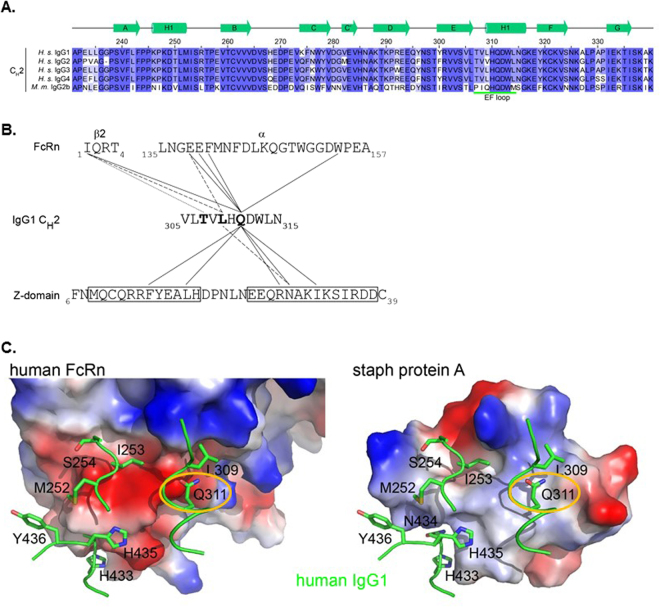
Figure 1.
Rationale for Mutations. (A) Sequence alignment of the CH2 domains of human IgG and mouse IgG2b. Secondary structures are based on those from PDB ID 1L6X and are shown in green above the alignments. The EF loop, which interacts with Z-doman and FcRn is underlined in green. Residue numbering follows the EU nomenclature. (B) Interactions of T307, L309, and Q311 with FcRn or Z-domain. T307, L309, and Q311 (bold) reside in the CH2 domain of the Fc. Each makes side-chain interactions with residues in FcRn (based on PDB ID 4N0U) and with the Z34C peptide, which is a disulfide-bonded two helix bundle derived from Z-domain (from PDB ID 1L6X) based on cutoff distance of 5 Å. T307 interacts with I1 from the β2 microglobulin of FcRn. L309 and Q311R are responsible for interactions with both FcRn and Z-domain (dashed and solid lines for L309 and Q311, respectively). (C) Comparison of the electrostatic surface encountered by the Fc when bound to human FcRn (left) or Z-domain (right). IgG residues are shown in green. Q311 (circled) interacts with different surfaces on FcRn vs. Z-domain.