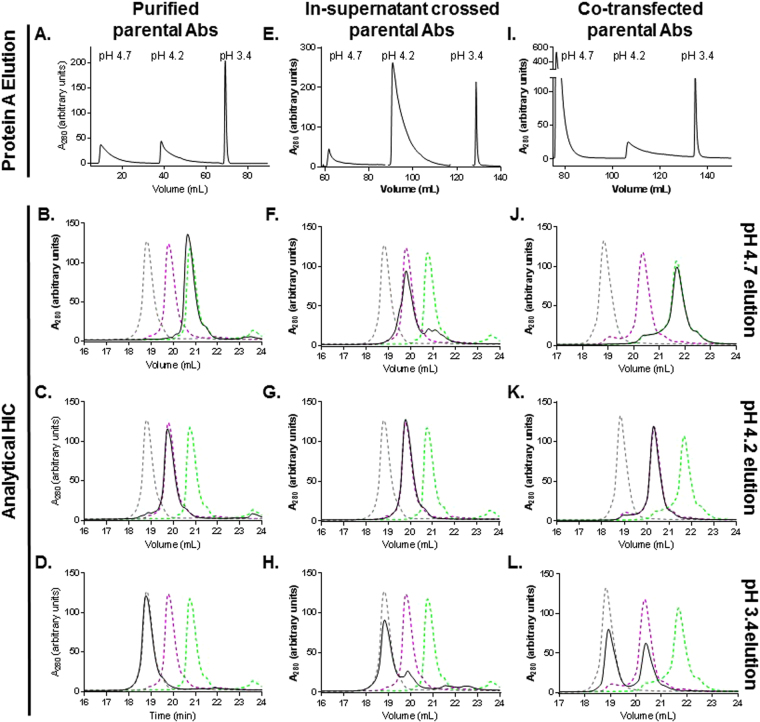
Figure 5.
TLQ mutations allow rapid isolation of BsAb. (A,E,I) Differential protein A purification of Ab mixtures using pH step gradients. Absorbance at 280 nm is monitored vs elution volume (mL). (B–D, F–H, J–L) Analytical hydrophobic interaction chromatography analysis of elution peaks from (A,E, I). (A–D) Purification of a BsAb made by cFAE of purified parental Abs. The TLQ mutant contained an F405L mutation while the “wild-type” molecule contained the K409R mutation. Elution from protein A affinity column monitored by absorbance at 280 nm (A). The pH of each elution step is indicated. (B–D) Protein A affinity elution peaks at pH 4.7, pH 4.2, and pH 3. were analyzed by HIC and are shown in black solid lines. The elution traces of the wild-type parental Ab (black dashed line), the TLQ parental Ab (green dashed line) and the BsAb (purple dashed line) are shown as references. (E–H) Purification of TLQ BsAb from in-supernatant cFAE. (E) Elution from protein A affinity column. Protein A affinity chromatography elutions at pH 4.7 (F), pH 4.2 (G), pH 3.4 (H) were analyzed by HIC. (I–L) Purification of T307P, L309Q, Q311R BsAb from co-transfected parental mAbs. The TLQ Ab and the wild-type Ab contained no additional mutations for pairing. (I) Elution from protein A column monitored by absorbance at 280 nm. Protein A elutions at pH 4.7 (J), pH 4.2 (K), pH 3.4 (L) were analyzed by HIC.