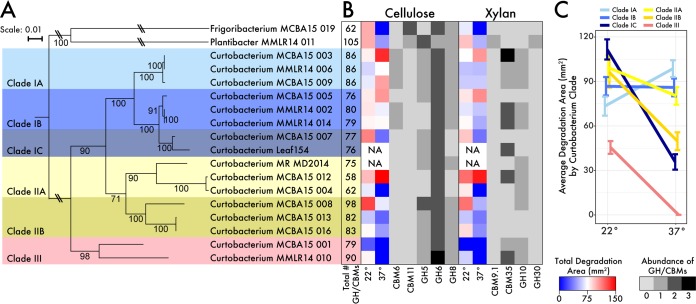
FIG 1 .
Phylogeny and traits of Curtobacterium strains. (A) Multilocus phylogenetic analysis using a concatenated alignment of 29 single-copy marker genes. Bar, 0.01 amino acid substitutions per position. (B) Genomic and physiological metrics of carbohydrate utilization. The total number of GH/CBM families targeting all potential carbohydrate substrates is shown in the first column. The physiological ability to degrade cellulose and xylan is shown in blue or red, while the genomic potential (presence of GH/CBM families) to degrade either cellulose or xylan is represented in gray or black. Strains that were not assayed (NA) for carbon degradation are indicated. (C) Average degradation area (±1 standard deviation [SD] [error bar]) of the substrates by Curtobacterium clade at each temperature.